1 Chapter 1 Chemistry On The Pyrimidine Ring
... The oxidation of dihydroorotate to form orotate is catalyzed by the flavoprotein dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHOD). There are three classes of DHODs. Class 1A DHODs are cytosolic homodimeric proteins that contain FMN and use fumarate as their oxidizing substrate (11). Class 1B enzymes are heterot ...
... The oxidation of dihydroorotate to form orotate is catalyzed by the flavoprotein dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHOD). There are three classes of DHODs. Class 1A DHODs are cytosolic homodimeric proteins that contain FMN and use fumarate as their oxidizing substrate (11). Class 1B enzymes are heterot ...
ARTICLES
... The 32-38 pair controls misreading of GUC near-cognate codon As sequence variation in the 32-38 pair did not affect decoding efficiency, we turned our investigation toward its decoding fidelity. The wobble pairing at the second G35 in tRNAAla GGC to a near-cognate valine codon, GUC, would be expecte ...
... The 32-38 pair controls misreading of GUC near-cognate codon As sequence variation in the 32-38 pair did not affect decoding efficiency, we turned our investigation toward its decoding fidelity. The wobble pairing at the second G35 in tRNAAla GGC to a near-cognate valine codon, GUC, would be expecte ...
Modified uridine at wobble position in tRNA of
... Ψ55 in E. coli tRNAs does not significantly affect the exponential growth, but a growth disadvantage is revealed when the mutant is grown in competition with the isogenic wild-type strain. A point mutation in the truB gene does not restore formation of the Ψ55, but efficiently compensates the growth ...
... Ψ55 in E. coli tRNAs does not significantly affect the exponential growth, but a growth disadvantage is revealed when the mutant is grown in competition with the isogenic wild-type strain. A point mutation in the truB gene does not restore formation of the Ψ55, but efficiently compensates the growth ...
Enzyme Mechanisms - Weber State University
... • Carbonic Anhydrase contains an important cofactor at the active site, namely a zinc ion, that helps activate water molecules prior to their reaction with CO2. ...
... • Carbonic Anhydrase contains an important cofactor at the active site, namely a zinc ion, that helps activate water molecules prior to their reaction with CO2. ...
ABSTRACT Title of Document: PROGRAMMED
... in the cell, but it certainly isn’t simple. After genes are transcribed into mRNAs, the ribosome is responsible for converting the information contained in nucleotide sequences to amino acids to form proteins. Ribosomes are thus essential to all forms of life. The ribosome is a complex machine made ...
... in the cell, but it certainly isn’t simple. After genes are transcribed into mRNAs, the ribosome is responsible for converting the information contained in nucleotide sequences to amino acids to form proteins. Ribosomes are thus essential to all forms of life. The ribosome is a complex machine made ...
Major players on the microbial stage: why archaea
... archaeal and bacterial partners in the event have varied (Forterre, 2010). Most recently, the archaeal partner has been suggested to be a member of the Thaumarchaeota, since these organisms possess a number of eukaryotic features not found in other archaeal phyla (Forterre, 2010). However, other mod ...
... archaeal and bacterial partners in the event have varied (Forterre, 2010). Most recently, the archaeal partner has been suggested to be a member of the Thaumarchaeota, since these organisms possess a number of eukaryotic features not found in other archaeal phyla (Forterre, 2010). However, other mod ...
Identity elements in tRNA-mediated transcription
... Fig. 3. Effect of native and chimeric tRNAs on transcription antitermination in the trpE-lacZ fusion. RNA was isolated from L. lactis cells after a growth medium shift as indicated in Methods and used to prepare a Northern blot that was hybridized with a lacZ-specific probe to visualize full length ...
... Fig. 3. Effect of native and chimeric tRNAs on transcription antitermination in the trpE-lacZ fusion. RNA was isolated from L. lactis cells after a growth medium shift as indicated in Methods and used to prepare a Northern blot that was hybridized with a lacZ-specific probe to visualize full length ...
Identity elements in tRNA-mediated transcription
... Fig. 3. Effect of native and chimeric tRNAs on transcription antitermination in the trpE-lacZ fusion. RNA was isolated from L. lactis cells after a growth medium shift as indicated in Methods and used to prepare a Northern blot that was hybridized with a lacZ-specific probe to visualize full length ...
... Fig. 3. Effect of native and chimeric tRNAs on transcription antitermination in the trpE-lacZ fusion. RNA was isolated from L. lactis cells after a growth medium shift as indicated in Methods and used to prepare a Northern blot that was hybridized with a lacZ-specific probe to visualize full length ...
arXiv:0708.2724v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Aug 2007
... chemical techniques and physical differences of strands of DNA. Most importantly, these proposals challenge our understanding of, and ability to manipulate and probe, physical processes at the interface between solids, liquids, and biomolecules down to the nanometer scale regime (Di Ventra et al., 2 ...
... chemical techniques and physical differences of strands of DNA. Most importantly, these proposals challenge our understanding of, and ability to manipulate and probe, physical processes at the interface between solids, liquids, and biomolecules down to the nanometer scale regime (Di Ventra et al., 2 ...
Full-Text PDF
... enzymatic polymerization was conducted in the presence of the guest polymers. Since the structure of this polymeric system is similar to the way that a plant vine twines around a rod, this polymerization system has been named “vine-twining polymerization”. Through this approach, amylose supramolecul ...
... enzymatic polymerization was conducted in the presence of the guest polymers. Since the structure of this polymeric system is similar to the way that a plant vine twines around a rod, this polymerization system has been named “vine-twining polymerization”. Through this approach, amylose supramolecul ...
Document
... are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Computational Identification of Plant MicroRNAs and
... plant miRNAs have a strong propensity to target genes controlling development, particularly those of transcription factors and F-box proteins. However, plant miRNAs have conserved regulatory functions extending beyond development, in that they also target superoxide dismutases, laccases, and ATP sul ...
... plant miRNAs have a strong propensity to target genes controlling development, particularly those of transcription factors and F-box proteins. However, plant miRNAs have conserved regulatory functions extending beyond development, in that they also target superoxide dismutases, laccases, and ATP sul ...
The enhancement of ribosomal transcription by the recycling of RNA
... pre-ribosomal RNA, (40S pre-rRNA), but continues through the sequences lying downstream of the 28S gene, (7,8). The transcription is eventually terminated just 213 b.p. upstream of the pre-rRNA promoter for the following gene unit in the tandem gene array, site "T" in fig. 1, i.e. the same site at w ...
... pre-ribosomal RNA, (40S pre-rRNA), but continues through the sequences lying downstream of the 28S gene, (7,8). The transcription is eventually terminated just 213 b.p. upstream of the pre-rRNA promoter for the following gene unit in the tandem gene array, site "T" in fig. 1, i.e. the same site at w ...
Par-1
... machinery Many components of RNAi machinery have been identified through genetic screening for RNAi defective mutants and through biochemical studies using cell extracts (e.g. Drosophila embryo extract). ...
... machinery Many components of RNAi machinery have been identified through genetic screening for RNAi defective mutants and through biochemical studies using cell extracts (e.g. Drosophila embryo extract). ...
p68/DDX5 DEAD-box RNA helicase gene encodes a novel miRNA
... that while p68 RNA helicase activity appears to be important for some functions (e.g., RNA processing), it does not appear to be required for its role as a transcriptional coactivator. The p68 gene contains a large intron (intron 11, 1.2 kb in the human gene), which has been conserved through evolut ...
... that while p68 RNA helicase activity appears to be important for some functions (e.g., RNA processing), it does not appear to be required for its role as a transcriptional coactivator. The p68 gene contains a large intron (intron 11, 1.2 kb in the human gene), which has been conserved through evolut ...
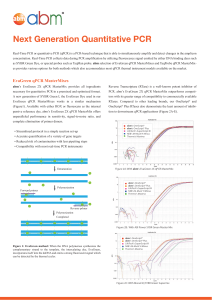
Next Generation Quantitative PCR
... as SYBR Green Dye, or special probes such as TaqMan probe. abm selection of EvaGreen qPCR MasterMixes and TaqProbe qPCR MasterMixes provides various options for both methods which also accommodates most qPCR thermal instrument models available on the market. ...
... as SYBR Green Dye, or special probes such as TaqMan probe. abm selection of EvaGreen qPCR MasterMixes and TaqProbe qPCR MasterMixes provides various options for both methods which also accommodates most qPCR thermal instrument models available on the market. ...
Syntabulin, a motor protein linker, controls dorsal
... disorganized vegetal microtubule array formation, and subsequently displays ventralization (Mei et al., 2009). Furthermore, a ubiquitin ligase, tripartite motif-containing 36 (trim36), is localized to the vegetal cortex of Xenopus oocytes, and when depleted causes defective vegetal microtubule array ...
... disorganized vegetal microtubule array formation, and subsequently displays ventralization (Mei et al., 2009). Furthermore, a ubiquitin ligase, tripartite motif-containing 36 (trim36), is localized to the vegetal cortex of Xenopus oocytes, and when depleted causes defective vegetal microtubule array ...
Endonucleolytic processing of CCAless tRNA precursors by RNase
... that the decrease in YqjK levels leads to the accumulation of tRNA precursors with 3¢ extensions. We noticed a relatively good correlation between whether or not a precursor RNA accumulated in the absence of IPTG and whether the corresponding tRNA gene had an encoded CCA motif. With one possible exc ...
... that the decrease in YqjK levels leads to the accumulation of tRNA precursors with 3¢ extensions. We noticed a relatively good correlation between whether or not a precursor RNA accumulated in the absence of IPTG and whether the corresponding tRNA gene had an encoded CCA motif. With one possible exc ...
Prokaryotic features of a nucleus
... [16] demonstrated that the aminoterminal and carboxyterminal moieties of the GAPDH polypeptide are organized as two independent three-dimensional units, which were highly conserved during the divergence of prokaryotes and eukaryotes: the coenzyme-binding domain, which has a similar structure in all ...
... [16] demonstrated that the aminoterminal and carboxyterminal moieties of the GAPDH polypeptide are organized as two independent three-dimensional units, which were highly conserved during the divergence of prokaryotes and eukaryotes: the coenzyme-binding domain, which has a similar structure in all ...
Mutations at the Darkener of apricot Locus Modulate Transcript
... 1993; ZACHAR, CHoU and BINGHAM1987). In general, the products of second-site modifier loci play a role in the expression of the mutation-causing transposable element, and in modifying its activity, result in an alteration of the mutant phenotype. We are seeking to understand the functions these modi ...
... 1993; ZACHAR, CHoU and BINGHAM1987). In general, the products of second-site modifier loci play a role in the expression of the mutation-causing transposable element, and in modifying its activity, result in an alteration of the mutant phenotype. We are seeking to understand the functions these modi ...
Potential alteration of U37K paleothermometer due to selective
... temperature is sometimes not so clear cut and several discrepancies between alkenone-derived SSTs and those derived from other proxies such oxygen isotopes or foraminiferal assemblages (Volkman, 2000) or with mean SSTs (Conte et al., 1992, 2001; Gong & Hollander, 1999; RosellMelé et al., 2000; Hara ...
... temperature is sometimes not so clear cut and several discrepancies between alkenone-derived SSTs and those derived from other proxies such oxygen isotopes or foraminiferal assemblages (Volkman, 2000) or with mean SSTs (Conte et al., 1992, 2001; Gong & Hollander, 1999; RosellMelé et al., 2000; Hara ...
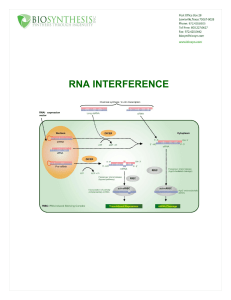
RNA interference - Bio
... ODNs- ODNs are generally ~20 nucleotides in length, their mode of action is by hybridizing to pre-mRNA and mRNA to produce a substrate for ribonuclease H (RNaseH) which specifically degrades the RNA strand of the formed RNA-DNA duplexes. Modification of ODN’s in a way to prevent the action of RNaseH ...
... ODNs- ODNs are generally ~20 nucleotides in length, their mode of action is by hybridizing to pre-mRNA and mRNA to produce a substrate for ribonuclease H (RNaseH) which specifically degrades the RNA strand of the formed RNA-DNA duplexes. Modification of ODN’s in a way to prevent the action of RNaseH ...
Introduction to the BLAST Suite and BLASTN
... The COMMENT section may include information such as accession numbers of related sequences or references to other databases. In this patent record, it repeats basic details about the patent. The last section of this file is the DNA sequence. It is one continuous sequence, broken up into groups of 10 ...
... The COMMENT section may include information such as accession numbers of related sequences or references to other databases. In this patent record, it repeats basic details about the patent. The last section of this file is the DNA sequence. It is one continuous sequence, broken up into groups of 10 ...
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to a messenger RNA The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene finishes, or terminates. The 3'-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3' end. In some genes, these proteins may add a poly(A) tail at any one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing.The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear export, translation, and stability of mRNA. The tail is shortened over time, and, when it is short enough, the mRNA is enzymatically degraded. However, in a few cell types, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails are stored for later activation by re-polyadenylation in the cytosol. In contrast, when polyadenylation occurs in bacteria, it promotes RNA degradation. This is also sometimes the case for eukaryotic non-coding RNAs.mRNA molecules in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have polyadenylated 3'-ends, with the prokaryotic poly(A) tails generally shorter and less mRNA molecules polyadenylated.








![arXiv:0708.2724v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Aug 2007](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014946021_1-c477dba1add7a260e278ca181f537c79-300x300.png)