* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
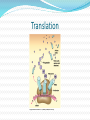
Transcription & Translation Transcription DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is complementary to the DNA base pairs. The enzyme used is RNA polymerase Transcription Translation Protein being made from the RNA template RNA messenger= carries message from DNA Ribosomal RNA= ribosome that reads the mRNA Transfer RNA= transfers the amino acid from the code of nitrogen bases Steps of Translation 1. mRNA finds a ribosome 2. mRNA is read by the ribosome 3. Every 3 bases = codon 4. Each codon read = 1 amino acid brought by the tRNA (3 bases on anticodon) 5. Many amino acids strung together = polypeptide = protein Translation Initiation- Small ribosome subunit finds bases AUG, then the large subunit binds and starts the process Elongation- Amino acids are bonded by peptide bonds Termination- Stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) signals the release of the polypeptide from the ribosome Translation Transcription & Translation