Determining the Transcription Factor Genes Populating a Fruit Fly
... The methodological goal of the RNAi screen was to reduce the expression of Drosophila melanogaster transcription factor genes individually along the dorsal midline of the abdomen. The reduction of gene expression occurs through the exploitation of the endogenous fruit fly RNA interference pathway. I ...
... The methodological goal of the RNAi screen was to reduce the expression of Drosophila melanogaster transcription factor genes individually along the dorsal midline of the abdomen. The reduction of gene expression occurs through the exploitation of the endogenous fruit fly RNA interference pathway. I ...
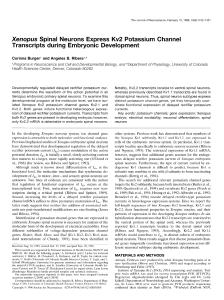
Xenopus Spinal Neurons Express Kv2 Potassium Channel
... domains. Screening of axenopus tadpole brain cDNA library with pXb3 and pXb4 probes identifies two clones, initially called XShab9 and XShabl2, which contain fulllength coding sequences. XShab9 has a 3.2 kb insert that includes 2628 bp of coding region (Fig. L4), 153 bp of .5’-UTR, and 428 bp of 3’. ...
... domains. Screening of axenopus tadpole brain cDNA library with pXb3 and pXb4 probes identifies two clones, initially called XShab9 and XShabl2, which contain fulllength coding sequences. XShab9 has a 3.2 kb insert that includes 2628 bp of coding region (Fig. L4), 153 bp of .5’-UTR, and 428 bp of 3’. ...
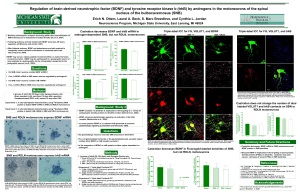
If so, is trkB mRNA in SNB motor neurons
... Immunorectivity for trkB was observed in SNB motoneurons. Many terminals contacting SNB motoneurons contained VGLUT1 and trkB. Red arrowheads: trkB immunoreactivity in SNB soma. White arrowheads: VGLUT1-positive appositions to SNB dendrites. White arrows: terminal structures positive for both VGLUT1 ...
... Immunorectivity for trkB was observed in SNB motoneurons. Many terminals contacting SNB motoneurons contained VGLUT1 and trkB. Red arrowheads: trkB immunoreactivity in SNB soma. White arrowheads: VGLUT1-positive appositions to SNB dendrites. White arrows: terminal structures positive for both VGLUT1 ...
as Adobe PDF - Edinburgh Research Explorer
... the specification of subtypes of VM in mice (Lettice et al. 1999) and flies (Azpiazu and Frasch 1993). This high level of functional conservation suggests that the underlying transcriptional circuitry governing VM development may also be conserved. To date, most progress has been made in elucidating ...
... the specification of subtypes of VM in mice (Lettice et al. 1999) and flies (Azpiazu and Frasch 1993). This high level of functional conservation suggests that the underlying transcriptional circuitry governing VM development may also be conserved. To date, most progress has been made in elucidating ...
Alternatively Spliced Genes
... that pre-mRNA splicing and alternative splicing play critical roles in regulating gene expression and in enhancing genetic diversity. Evolutionarily, the basic machinery for pre-mRNA splicing appears to be highly conserved among different species of metazoans. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, although o ...
... that pre-mRNA splicing and alternative splicing play critical roles in regulating gene expression and in enhancing genetic diversity. Evolutionarily, the basic machinery for pre-mRNA splicing appears to be highly conserved among different species of metazoans. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, although o ...
The Bacterial Toxin RelE Displays Codon
... of protein synthesis by RelE in vivo. We have found that although RelE does not degrade free RNA, it cleaves mRNA in the ribosomal A site with high codon specificity. Among stop codons UAG is cleaved with fast, UAA intermediate and UGA slow rate, while UCG and CAG are cleaved most rapidly among sens ...
... of protein synthesis by RelE in vivo. We have found that although RelE does not degrade free RNA, it cleaves mRNA in the ribosomal A site with high codon specificity. Among stop codons UAG is cleaved with fast, UAA intermediate and UGA slow rate, while UCG and CAG are cleaved most rapidly among sens ...
ABA overlysensitive5 (ABO5), encoding a pentatricopeptide repeat
... genes. Plant mitochondria have specific alternative respiratory pathways, including the non-proton-pumping NAD(P)H dehydrogenases, which bypass complex I for diminishing ROS production, and an alternative oxidase (AOX), which directly accepts electrons from the ubiquinone pool for reducing ROS produ ...
... genes. Plant mitochondria have specific alternative respiratory pathways, including the non-proton-pumping NAD(P)H dehydrogenases, which bypass complex I for diminishing ROS production, and an alternative oxidase (AOX), which directly accepts electrons from the ubiquinone pool for reducing ROS produ ...
Modified uridine at wobble position in tRNA of
... which are derivatives of the four normal nucleosides, adenosine (A), guanosine (G), cytidine (C), and uridine (U). Although modified nucleosides are present at many positions in tRNAs, two positions in the anticodon region, position 34 (wobble position) and position 37, show the largest variety of m ...
... which are derivatives of the four normal nucleosides, adenosine (A), guanosine (G), cytidine (C), and uridine (U). Although modified nucleosides are present at many positions in tRNAs, two positions in the anticodon region, position 34 (wobble position) and position 37, show the largest variety of m ...
Neurospora Spore Killers Sk-2 and Sk
... only partial resistance to Sk-2 killing when acting alone. However, when paired with a modifier allele, mod(pr), pr(Sk-2) confers a high level of resistance. In a wild-type cross (i.e., in the absence of a Spore killer), the resistant alleles do not affect crossover frequencies and can therefore be ...
... only partial resistance to Sk-2 killing when acting alone. However, when paired with a modifier allele, mod(pr), pr(Sk-2) confers a high level of resistance. In a wild-type cross (i.e., in the absence of a Spore killer), the resistant alleles do not affect crossover frequencies and can therefore be ...
Molecular Network Controlling the Ovule Development in
... take place within the ovule. In the ovule both sporophytic and gametophytic generation coexist. The analyses of this developmental process provides an excellent tool to understand the molecular mechanism involved in controlling the basic processes like primordia initiation, specification, cell divis ...
... take place within the ovule. In the ovule both sporophytic and gametophytic generation coexist. The analyses of this developmental process provides an excellent tool to understand the molecular mechanism involved in controlling the basic processes like primordia initiation, specification, cell divis ...
Imposition of Crossover Interference through the
... Our study provides strong evidence that synapsis initiation and crossing over occur at the same sites on chromosomes. First, and most compelling, we have found that SICs display interference, just like COs. In addition, SICs tend to be reduced in frequency near centromeres, and they are found at hig ...
... Our study provides strong evidence that synapsis initiation and crossing over occur at the same sites on chromosomes. First, and most compelling, we have found that SICs display interference, just like COs. In addition, SICs tend to be reduced in frequency near centromeres, and they are found at hig ...
The role of Grainy head in epithelial tissue growth
... The grainy head (grh) gene family encodes an important group of transcription factors that play a remarkably conserved role in epithelial organ development, epithelial barrier formation and epithelial repair upon damage in different organisms. The regulation and molecular targets of Grh are numerous ...
... The grainy head (grh) gene family encodes an important group of transcription factors that play a remarkably conserved role in epithelial organ development, epithelial barrier formation and epithelial repair upon damage in different organisms. The regulation and molecular targets of Grh are numerous ...
An AT-hook gene is required for palea formation and floral organ
... Consistent with this controversy of sepal equivalent organ in rice and other grasses, class A genes in rice remain difficult to determine. Similar to rice, the maize outer whorl organ identity remains elusive that molecular dissection of regulatory pathways has just started (Thompson et al., 2009; Wh ...
... Consistent with this controversy of sepal equivalent organ in rice and other grasses, class A genes in rice remain difficult to determine. Similar to rice, the maize outer whorl organ identity remains elusive that molecular dissection of regulatory pathways has just started (Thompson et al., 2009; Wh ...
34386 - PubAg
... Cortesia marginiventris, a parasitic wasp that attacks larvae of several species of Lepidoptera. Two elicitors have been identified in the oral secretions of insect herbivores that trigger the production of volatiles. Mattiacci et al. (8) found that a -glucosidase in Pieris brassicae caterpillars e ...
... Cortesia marginiventris, a parasitic wasp that attacks larvae of several species of Lepidoptera. Two elicitors have been identified in the oral secretions of insect herbivores that trigger the production of volatiles. Mattiacci et al. (8) found that a -glucosidase in Pieris brassicae caterpillars e ...
Function and Control of the Spx-Family of Proteins Within
... “ArsC–ArsC” grouping that includes the bona fide arsenate reductase from E. coli and its orthologs from a variety of Gram-positive and -negative species. Mutations in a gene encoding an ArsC-like protein were reported in Lactococcus lactis (Duwat et al. 1999). The mutation elevated temperature resis ...
... “ArsC–ArsC” grouping that includes the bona fide arsenate reductase from E. coli and its orthologs from a variety of Gram-positive and -negative species. Mutations in a gene encoding an ArsC-like protein were reported in Lactococcus lactis (Duwat et al. 1999). The mutation elevated temperature resis ...
Origin of the catalytic activity of bovine seminal ribonuclease against
... N103K), b ) A(A19S L35M K37Q N103K), c ) A(T3S A19S K37Q N103K), d ) A(T3S A19S K37Q N103E), e ) A(T3S S15P A19S K31Q K37Q S59F T70S Y76N T78A S80H A96V N103E), f ) A(T3S A19S K37Q N103E), g ) A(T3S A19S K37Q Y76N S80R N103E), h1 ) A(T3S S16G T17S A19S A20S N34K L35M K37Q D38G A64T Y76N S80R A102V N ...
... N103K), b ) A(A19S L35M K37Q N103K), c ) A(T3S A19S K37Q N103K), d ) A(T3S A19S K37Q N103E), e ) A(T3S S15P A19S K31Q K37Q S59F T70S Y76N T78A S80H A96V N103E), f ) A(T3S A19S K37Q N103E), g ) A(T3S A19S K37Q Y76N S80R N103E), h1 ) A(T3S S16G T17S A19S A20S N34K L35M K37Q D38G A64T Y76N S80R A102V N ...
Landick R, Yanofsky C. 1987. Transcription
... attenuator. This decision is based on the cellular level of charged tRNA Trp. Under starvation conditions, in which all tRNATrp essentially is uncharged, the rate of read through transcription at the attenuator increases about eightfold over the rate observed when tRNATrp is fully charged. We do not ...
... attenuator. This decision is based on the cellular level of charged tRNA Trp. Under starvation conditions, in which all tRNATrp essentially is uncharged, the rate of read through transcription at the attenuator increases about eightfold over the rate observed when tRNATrp is fully charged. We do not ...
PH4 of Petunia Is an R2R3 MYB Protein That Activates
... of the pathway, in all pigmented tissues (Quattrocchio et al., 1993) and encode a basic-helix-loop-helix (BHLH) transcription factor and a WD40 protein, respectively (de Vetten et al., 1997; Spelt et al., 2000). AN2 encodes a MYB-type transcription factor whose function appears to be (partially) red ...
... of the pathway, in all pigmented tissues (Quattrocchio et al., 1993) and encode a basic-helix-loop-helix (BHLH) transcription factor and a WD40 protein, respectively (de Vetten et al., 1997; Spelt et al., 2000). AN2 encodes a MYB-type transcription factor whose function appears to be (partially) red ...
Endonucleolytic processing of CCAless tRNA precursors by RNase
... To get an idea of what proportion of B.subtilis tRNAs might be affected by the decrease in yqjK expression, speci®c oligonucleotide probes were designed for 11 more tRNAs. As can be seen from the northern blot in Figure 3, precursor species accumulate for ®ve of these tRNAs in the RNA samples isolat ...
... To get an idea of what proportion of B.subtilis tRNAs might be affected by the decrease in yqjK expression, speci®c oligonucleotide probes were designed for 11 more tRNAs. As can be seen from the northern blot in Figure 3, precursor species accumulate for ®ve of these tRNAs in the RNA samples isolat ...
Comparative analysis of different TaqMan real-time RT
... The sensitivity of these detection assays can be affected by the quality of extracted RNA, RNase contamination or RT-PCR inhibitors in environmental and clinical samples, especially in faecal material (Escobar-Herrera et al. 2006; Rutjes et al. 2007; Scipioni et al. 2008). Failure to amplify the vir ...
... The sensitivity of these detection assays can be affected by the quality of extracted RNA, RNase contamination or RT-PCR inhibitors in environmental and clinical samples, especially in faecal material (Escobar-Herrera et al. 2006; Rutjes et al. 2007; Scipioni et al. 2008). Failure to amplify the vir ...
A MIAME-compliant Microarray Database
... • Design a series of Affymetrix chips that covers the entire genome! • Run RNA extracts from plants under a wide range of conditions on these chips. • See which areas of the genome light up! ...
... • Design a series of Affymetrix chips that covers the entire genome! • Run RNA extracts from plants under a wide range of conditions on these chips. • See which areas of the genome light up! ...
Document
... 8- Do VIROIDs die? NO, however like all nucleic acids, their structure can be degraded by catalysts or UV light 9- Do VIROIDs come from pre-existing viroids? YES ~ existing VIROIDs are the templates for the next generation of replicants ...
... 8- Do VIROIDs die? NO, however like all nucleic acids, their structure can be degraded by catalysts or UV light 9- Do VIROIDs come from pre-existing viroids? YES ~ existing VIROIDs are the templates for the next generation of replicants ...
Next Generation Quantitative PCR
... abm’s ExCellenCT Lysis Kit 5X All-In-One RT MasterMix (with ExCellenCT Lysys Kit) ...
... abm’s ExCellenCT Lysis Kit 5X All-In-One RT MasterMix (with ExCellenCT Lysys Kit) ...
Risk assessment - Office of the Gene Technology Regulator
... identified when a hazard is considered to have some chance of causing harm. Those events that do not lead to an adverse outcome, or could not reasonably occur, do not advance in the risk assessment process. Sixteen events were identified and assessed whereby the release of the GM sugarcane lines mig ...
... identified when a hazard is considered to have some chance of causing harm. Those events that do not lead to an adverse outcome, or could not reasonably occur, do not advance in the risk assessment process. Sixteen events were identified and assessed whereby the release of the GM sugarcane lines mig ...
a complex voyage to the X chromosome
... genomics: how do chromatin regulators recognize their targets within a complex genome? This review will focus on the dosage compensation machinery in Drosophila, known as the male-specific lethal (MSL) complex, and on how this ribonucleoprotein complex recognizes the male X chromosome. The giant pol ...
... genomics: how do chromatin regulators recognize their targets within a complex genome? This review will focus on the dosage compensation machinery in Drosophila, known as the male-specific lethal (MSL) complex, and on how this ribonucleoprotein complex recognizes the male X chromosome. The giant pol ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.