* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LAB 5 – CORONAL 1 (Jan 29)
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Orbitofrontal cortex wikipedia , lookup
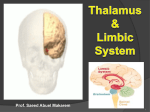
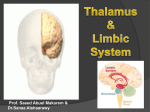
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
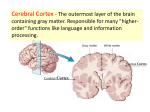
Cerebral cortex wikipedia , lookup
LAB 8 – CORONAL 4 (Mar 5) Corpus Callosum The sweeping band (commissure) of white matter that provides a connection between the two halves of the cerebrum in the brain. It enables the transfer of information from one cerebral hemisphere to the other. Cingulate Gyrus A gyrus within the longitudinal fissure above and almost surrounding the corpus callosum . It is part of the limbic system and is involved in pain sensations, control of visceral responses associated with emotions, and the planning of motor actions. Lateral Ventricle The two lateral ventricles in the forebrain, the main parts of which lie in the temporal lobes immediately below the corpus callosum and above the thalamus, are separated by the septum pellucidum Caudate Nucleus One of the basal ganglia in the corpus striatum : a crescent-shaped mass of grey matter in each cerebral hemisphere, near the thalamus, concerned with inhibitory control of movement. See also attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder Internal Capsule Either of two neural pathways in the brain between the thalamus and the lenticular nucleus containing nerve fibres running from the thalamus to the left or right cerebral cortex and from the cerebral cortex to the thalamus, brainstem, and spinal cord. It is a common site for a stroke . External Capsule layer of nerve fibres between the lentiform nucleus and the claustrum (lentiform) belonging to the basal ganglia located lateral to the internal capsule. Two parts: putamen and globus pallidus) Claustrum Either of two thin sheets of grey matter, composed chiefly of spindle cells, separating the internal capsule from the insula (limbic-anterior part functions as the cortical pain centre, and the posterior part is implicated in language functions) n either side of the lenticular nucleus at the base of the brain. Putamen One of the basal ganglia in the corpus striatum , a large reddish structure surrounding the globus pallidus on three sides in each cerebral hemisphere, consisting of the lateral part of the lenticular nucleus , implicated in posture and movement control. Septum Pellucidum A thin, double partition extending down from the lower surface of the corpus callosum to the fornix and adjacent structures, separating the lateral ventricles of the brain and enclosing an area above the third ventricle. It is part of the limbic system and one of the most important of the pleasure centres of the brain, electrical stimulation of this area producing intensely agreeable sensations of well-being in humans. Experimental rats with access to levers to control the output of electrodes implanted semi-permanently in their septal areas self-stimulate themselves for long periods to the virtual exclusion of food, sex, and sleep, whereas ablation of the area leads to septal rage . Globus Pallidus One of the basal ganglia in the lenticular nucleus of the corpus striatum, either of a pair of pale yellow globular masses involved in posture, muscle tonus, and the control of eating and drinking. Column & Body of the Fornix Any structure resembling an arch, especially the archlike band of white fibres in the limbic system at the base of the brain, projecting from the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies , involved in memory and the control of eating. Also called the vault. Optic Tract The part of each optic nerve between the optic chiasm and the lateral geniculate nucleus. Amygdala An almond-shaped brain structure in the limbic system at the base of the inside of each temporal lobe , contiguous with the olfactory cortex, controlling the experience and expression of emotion and involved in motivation, aggression, feeding, and (through its links with the hippocampus) long-term memory. Electrical stimulation of this area usually produces an intense emotion of fear. Ablation of the amygdala has been used to treat intermittent explosive disorder or other forms of impulse-control disorder. Anterior Thalamus Either of a pair of large, golfballsized capsules near the base of the brain in the diencephalon, forming a lateral wall of the third ventricle , containing all the nerve fibres that ascend and descend between the cortex and the spinal cord, part of the ascending reticular activating system , and relay stations such as the lateral geniculate nuclei and medial geniculate nuclei , and receiving all sensory inputs, except from the olfactory receptors, before they are relayed to areas in the cerebral cortex. Its ventral anterior nuclei and ventral lateral nuclei receive inputs from the globus pallidus and cerebellum and project to the prefrontal cortex and motor cortex, its ventral posterior nuclei contain inverted topographic maps of the body and project to the somatosensory cortex, and the pulvinar at its back is implicated in attention. Hypothalamus A fingernail-sized area of the diencephalon at the base of the brain in the limbic system, occupying the side walls and floor of the third ventricle, situated below both sides of the thalamus and above the pituitary gland, consisting of two halves with paired right and left nuclei, crucially involved in the regulation of the endocrine glands and the autonomic nervous system and implicated in the control of temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, hunger, thirst, sexual arousal, predatory aggression, and fight-or-flight responses.