* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
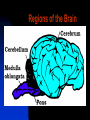
The Nervous System The Nervous System Functions of the nervous system include: coordination of the physical movements of the body corresponding to the action of the senses (hearing, tasting, smelling, touching, and sight) The Nervous System The Nervous System is composed of two major parts: the Central Nervous System the Peripheral Nervous System The Nervous System The Central Nervous System includes the brain and spinal cord. This system controls most of the voluntary responses of the animal. The Nervous System The brain controls the central nervous system. Parts of the brain include the : cerebrum cerebellum pons medulla oblongata Regions of the Brain The Nervous System The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum, which is usually large in relation to the body size in more intelligent animals. The cerebrum is responsible for the decisionmaking or thinking process that controls the voluntary muscles and reacts to the stimuli of the senses. The Nervous System The cerebellum serves as the coordinator of the messages from the other parts of the brain to the body. Reflex actions, like blinking, breathing, and swallowing are controlled by the pons and medulla oblongata. The Nervous System The spinal cord is the main organ used for impulse transferal between the brain and other parts of the body. The spinal cord is divided into segments, and from each segment a pair of spinal nerves extends to the body. The Nervous System The spinal cord receives messages from sensory nerve fibers from various parts of the body and transmits them to the brain. Efferent neurons (motor nerve fibers) in the spinal cord then transmit the responses from the brain back to the body. The Nervous System The peripheral nervous system controls the functions of body tissues and organs. Somatic nerves transmit signals from the outer parts of the body to the brain. Autonomic nerves help to control the functions of internal organs, like the heart and stomach. The Nervous System Nerve cells, called neurons, consist of a single, long fiber, called an axon, and several branched threads called dendrites. Sensory organs, like the skin, stimulate the dendrites through which a nerve impulse passes to the axon. The Nervous System The impulse may be conducted to an effector organ, like a muscle cell. The point where the dendrite is connected to the axon is called a synapse. Some impulses are not sent to the brain, but go directly to the effector organ. The Nervous System Nerves occur in single neurons or in bundles, called nerve trunks. Nerve cells that are found outside the brain and spinal cord are called ganglions. The Nervous System Nerve cells that receive stimuli and carry the impulses to the central nervous system are called sensory or afferent neurons. Nerve cells which carry messages from the brain to muscles or glands are called motor or efferent neurons.