* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
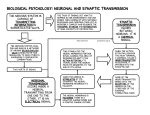
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Items 1. One assumption of phrenology is that (p32) 2. researcher interested in the functional specialization of different regions of the brain might conduct an experiment in which (p 32) 3. Paul’s grandmother has suffered a stroke and although she can understand him, she can’t communicate her own thoughts. Most likely Paul’s grandmother’s stroke was located in (p 33) 4. If a patient was able to speak and write, but couldn’t understand what anyone said to them, the most likely to be damaged is (p 33) 5. Originally, the case of Phineas Gage was used to argue against functional localization because (p 34) 6. Probably the most definitive evidence for the functional localization of brain areas came from the work of: (p 34) @ 7. One of the reasons that the homogeneity view of brain organization persisted for so long is that (p 35) 8. Brain lateralization refers to the fact that (p 36) 9. The lobe located at the very back of the head is the (p 37) 10. The lobe that is responsible for processing visual information is the (p 37) 11. While white matter is composed of ___________________, grey matter consists of ______________. (p 36) 12. The region of the brain where sensory inputs are processed to produce the perceptual experience is (p. 36-37) 13. A subcortical structure that is important in the transmission of sensory and motor information to and from the cortex is the (p 38) 14. Which brain area serves to coordinate and fine tune motor signals? (p, 38) 15. According to the law of specific nerve energies (p. 39) 16. According to the law of specific nerve energies (p. 39) 17. Which of the following is FALSE regarding sensory organization in the brain? (p 39) 18. Which of the following is FALSE regarding the topographic organization of sensory information in the brain? (p 40) 19. Which of the following is NOT consistent with contralateral representations? (p 40) 20. The soma of a neuron is responsible for (p 41) 21. What are the many branches of a neuron that receive information from other neurons called? (p 41) 22. Molly is sitting on the bank of a stream when she feels something slippery on her foot. This information is most likely processed by Molly’s (p 42). 23. Molly is sitting on the bank of a stream when she feels something slippery on her foot. She looks down and sees a salamander crawling over her toes. The recognition of the creature as a salamander is most likely processed by Molly’s (p 42-43). 24. Molly is sitting on the bank of a stream when she feels something slippery on her foot. She looks down and sees a salamander crawling over her toes. She quickly kicks her leg out, sending the salamander falling into the stream. Molly’s reaction to the salamander was most likely processed by her (p 42-43) 25. Which of the following is NOT one of the functions of glial cells? (p 43) 26. Other than neurons, the other major cell type found in the brain is (p 43) 27. Which of the following is true of oligodendrocytes? (p 43) 28. Which of the following provides the insulating material for axons in the peripheral nervous system? (p 43) 29. The membrane potential is defined as (p 44) 30. Which of the following is NOT a factor that affects the movement of ions across a cell membrane? (p 44) 31. Which of the following would contribute to the negative resting membrane potential of a neuron? (p 17) 32. Which of the following states is true regarding the resting membrane potential of a neuron? (45) 33. When the membrane potential becomes positive, this is called __________. (p 46) 34. What causes the membrane potential to be hyperpolarized? (p46) 35. What causes the membrane to be depolarized? (p 46) 36. Which of the following is NOT true regarding the action potential? (p 46) 37. Which of the following is an event that can trigger the initial Na+ influx that can cause the membrane potential to reach threshold? (p 46) 38. Which of the following do NOT occur with the action potential? (p 46) 39. The tiny gap that exists at the junction where two neurons meet is called the __________. (p 48) 40. Neurotransmitters are (p 48) 41. Which of the following is NOT true about the receptors on the postsynaptic neuron? (p 48) 42. One consequence of hyperpolarization is that the postsynaptic neuron is (p 49) 43. One reason that coding stimulus location for vision and touch is so automatic and effortless is because (p 50) 44. The receptive field is defined as (p 50) 45. A receptive field is always located on (p 50) 46. The brain can code for differences in stimulus intensity by (p 50-51) 47. Sensory adaptation occurs when (p 51) 48. Examining the firing of a neuron in the visual cortex of a cat by presenting different visual stimuli while a thin electrode records any electrical changes in that neuron is called (p 52) 49. Which of the following is an advantage of using single-unit recordings to understand brain function? (p 52) 50. Which of the following is an advantage of using EEG recordings to understand brain function? (p 53) 51. Presenting a participant with different visual stimuli while monitoring the electrical activity of groups of neurons through electrodes placed on the participant’s scalpis called (p 53). 52. Recording different levels of blood oxygen in the brain to produce an image based on the different resonance and relaxation process of molecules in the brain in response to the application of a strong magnetic field is called. (p 53-54). 53. Which of the following is a disadvantage of using fMRI to understand brain function? (p 54) 54. Injecting a participant with a form of radioactive water and then having the participant form various cognitive tasks is using (p 55-56) 55. Using a specialized video camera to measure differences in blood flow on the surface of the brain of a cat is using (p 56) 56. The major drawback of using optical imaging is that (p 56)@