* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurophysiology Complete
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
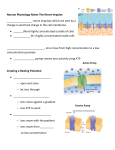
Neurophysiology Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses 2 major physiological properties of neurons: Excitability: the ability to respond to stimuli and convert it to nerve impulses Conductivity: the ability to transmit the impulse to other neurons, muscles or glands In a resting neuron, the outside is more positive than the inside Resting membrane potential: the difference in electrical charges that results in a voltage across the plasma membrane Polarized: a neuron at its resting membrane potential In the resting state, the predominant intracellular ion is K, Na is extracellular Resting membrane potential is maintained by the Na-K pump that transports Na and K in and out of the cell The Nerve Impulse Threshold stimulus: the membrane at the axon hillock becomes more permeable to Na ions when a neuron is activated by a stimulus of adequate intensity Depolarization: the interior becomes less negative, exterior becomes less positive Action potential: when depolarization reaches a certain point so that the membrane polarity changes Repolarization: within a millisecond Na and K return to their original state and the resting membrane potentil is restored Absolute refractory period: when the Na gates are open and the neuron is totally insensitive to additional stimuli Relative refractory period: if a very strong stimuli is able to reactivate the neuron after repolarization, it is called the relative refractory period Once an action potential begins, it is self propagating… it is NEVER PARTIALLY TRANSMITTED! Is an all or non response Nerve impulse: propagation of the action potential in neurons When a nerve impulse reaches the axon terminals, they release neurotransmitters that act to stimulate or inhibit the next neuron in the chain