* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
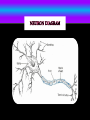
By: Alexandria J Max M Imanol S Detects information from the environment and controls body functions. MAJOR PARTS Brain: cerebrum, interprets input from the senses, controls movement, and carries out complex mental processes such as learning and remembering. Cerebellum: Coordinates the actions of your muscles and helps you keep your balance. Brain stem: Lies between the cerebellum and the spinal cord, controls your body’s involuntary actions those that occur automatically Spinal Cord: The spinal cord is the link between your brain and the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral Nervous system: Consist of a network of nerves that branch out from the central nervous system and connect it to the rest of the body Nerves: A bundle of fibers that transmits impulses of sensation to the brain or spinal cord, and impulses from these to the muscles and organs Neurons: Specialized to carry messages through an electrochemical process, in the human brain it has more than 100 billion neurons. THE PATHWAY A NERVE IMPULSE TRAVELS THROUGH THE BODY It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. HOW THE NERVOUS SYSTEM WORKS WITH OTHERS By sending commands to the other, and receiving information back from them. There are more nerve cells in the human brain than there are stars in the Milky Way If we lined up all the neuron in our body, it would be 600 miles long. There are 100 billion neurons in your brain alone. As we get older, there brain loses almost one gram a year.