* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Brain 101
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
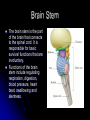
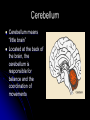
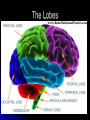
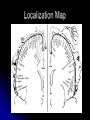
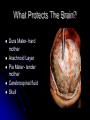
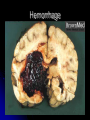
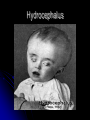
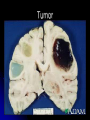
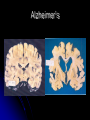
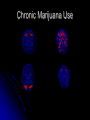
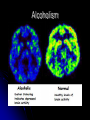
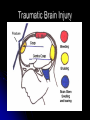
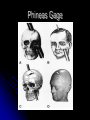
The Human Brain 101 Kristi Miller, M.S., L.P.T. A.K.A. “Gabriel’s Mom” Fun Brain Facts The average size of the adult brain is about 5.5 inches wide, 6.5 inches long, and 3.6 inches in height At birth, the brain weighs about 4/5 of a pound. The adult brain weighs about 3 lbs. The brain is 78% water There are 100 billion neurons in the human brain, the same number of stars in our galaxy More Fun Brain Facts The left hemisphere has 186 million more neurons than the right hemisphere The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph, as “slow” as Bugatti EB 16.4 Veyron which clocked at 253 mph More electrical impulses are generated in one day by the brain than by all the telephones in the world Even MORE Fun Brain Facts Albert Einstein’s brain weighed 1,230 grams (2.71 lbs), significantly less than the human average of 3 lbs The brain can stay alive for 4-6 minutes without oxygen. After that cells begin to die. After age 30, the brain shrinks a quarter of a percent (0.25%) in mass each year. History of Neuroanatomy Ancient references by Egyptians and Greeks Body mapping by Chinese Galen (129-201AD) named brain as seat of human spirit Renaissance dissection and illustrations 17th-19th century naming of brain anatomy Joseph Gall’s Phrenology spurs research 20th century developments (MRI, PET, SPECT) Methods of Study Selective surgical ablation or removal of brain tissue Faradic or galvanic (i.e. steady or pulsed) electrical stimulation of the brain Clinical studies of patients with disorders compared to evaluation of the brain after death EEG, CT, MRI, PET, SPECT and other computerized mapping of brain anatomy and activity Basic Brain Anatomy Brain Stem The brain stem is the part of the brain that connects to the spinal cord. It is responsible for basic survival functions that are involuntary. Functions of the brain stem include regulating respiration, digestion, blood pressure, heart beat, swallowing and alertness. Cerebellum Cerebellum means “little brain” Located at the back of the brain, the cerebellum is responsible for balance and the coordination of movements The Lobes Occipital Lobe The occipital lobe is located at the back of the brain The occipital lobe is responsible for processing visual reception as well as recognition of shapes and colors Parietal Lobes The parietal lobes contain the primary sensory cortex which controls sensation (touch and pressure) and the secondary sensory cortex which interprets size, weight, shape and texture. The parietal lobes also contain the motor cortex which controls movement of the limbs. Temporal Lobes The temporal lobes are located on the sides of the head just above the ears. The temporal lobes are responsible for organizing stimuli and forming memory. The left temporal lobe is responsible for a person’s ability to use language The right temporal lobe is responsible for a person’s ability to form and interpret visual memory Frontal Lobe The frontal lobe is located where? The frontal lobe function develops or “matures” last. The frontal lobe is responsible for “executive function”. This includes organization, planning, problem solving, selective attention, impulse control and personality. Localization Map Got Brain Damage? What Protects The Brain? Dura Mater- hard mother Arachnoid Layer Pia Mater- tender mother Cerebrospinal fluid Skull What causes damage to the brain? TBI Anoxia Tumors Environmental toxins Strokes Infection Drug Use Electric shock Metabolic imbalance Hemorrhage Hydrocephalus Tumor Alzheimer’s Chronic Marijuana Use Alcoholism Traumatic Brain Injury Dysfunction Associated With Brain Damage Mobility Sensation Coordination Swallowing Vision Appetite Speech Learning Memory Problem Solving Personality Impulse Control Mood Anger management Sleep Attention Concentration Orientation Confusion Social function The Ultimate Case Study: Phineas Gage Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a 26 year old foreman of a track construction crew that was blasting granite to build a railroad. Gage was, by all reports, likeable prior to his accident. He was packing dynamite powder into a hole with a tamping rod when an explosion blew the rod through his skull Phineas Gage Phineas Gage Phineas Gage Gage was awake when he got to the hospital with the rod sticking out of his head He could walk and talk as normal He developed fever from infection, but did not die His behavior, however, was permanently changed. Phineas Gage Gage was frequently found wandering around town in the rain at night with no coat or shoes (not a good idea in Vermont). He is unreasonable, irritable, and uses vulgar language. His old employees can no longer work with him Women are NOT attracted to him any more Questions?