* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain - Central Connecticut State University
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
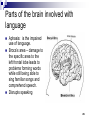
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
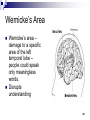
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
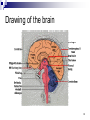
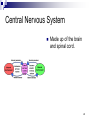
The Brain Part II 1 The Brain The Nervous System Made up of neurons communicating with other neurons 2 Drawing of the brain 3 Central Nervous System Made up of the brain and spinal cord. 4 Peripheral Nervous System somatic nervous system ANS Flight or fight controls the movements of our skeletal muscles Controls glands 5 Types of Nerves Nerves: Sensory Neurons Interneurons Motor Neurons 6 Somatic Nervous System Controls the movements of our skeletal muscles. 7 Peripheral Nervous System Consists of the somatic & ANS 8 ANS Controls the glands and the muscles of our internal organs. 9 Sympathetic & Parasympathetic Nervous System Sympathetic: arouses us for defense action Parasympathetic: It conserves energy as it calms you by decreasing your heartbeat, lowering your blood sugar, etc. 10 Endocrine System Endocrine system influences many aspects of our lives, e.g. growth, reproduction, metabolism, mood, working to keep everything in balance while we respond to stress, exertion, and even our own thoughts. 11 Hormones Secreted by the endocrine system – another form of chemical messenger. Influence our interest in sex, food, and aggression. 12 Adrenal Glands Located on top of the kidneys. Release epinephrine and norepinephrine (also called adrenaline and noradrenaline). 13 The brain stem & medulla The brain stem begins where the spinal cord enters the skull swelling slightly, forming the medulla. Here lies the controls for your heartbeat & breathing. 14 Pituitary Glands Pea-sized structure located in the base of the brain – controlled by the hypothalamus. 15 Reticular Formation Experiment: Moruzzi & Magoun – electrically stimulated the reticular formation of a sleeping cat The role of the reticular formation 16 Thalamus Thalamus = switching station Receives information from all the senses except smell and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, and touching. 17 Hippocampus Within the Limbic System, the hypothalamus influences hunger, regulates thirst, body temperature, and sexual behavior. 18 Amygdala If we electrically stimulate the amygdala (within the Limbic System). 1939 kluver & Bucy 19 Hypothalamus Olds & Milner (1954) – discovered that the hypothalamus was the “reward center”. 20 The role of Dopamine & pleasure Dopamine has been found in animal studies to be released when certain pleasures are taking place, e.g. sex, drinking, etc. 21 Addictive Behaviors? Some researchers believe that addictive disorders, such as alcoholism, drug abuse, and binge eating, may stem from a reward deficiency syndrome. 22 The Phineas Gage Story Frontal lobe damage was first connected to personality changes after the classic case of Phineas Gage. In 1848, a rod was shot up through his left cheek out of the top of his skull leaving his frontal lobe massively damaged. 23 Frontal Lobes The association areas within the frontal lobes helps us to judge, plan, and process new memories. 24 Parts of the brain involved with language Aphasia: is the impaired use of language. Broca’s area – damage to the specific area to the left frontal lobe leads to problems forming words while still being able to sing familiar songs and comprehend speech. Disrupts speaking 25 Wernicke’s Area Wernicke’s area – damage to a specific area of the left temporal lobe – people could speak only meaningless words. Disrupts understanding 26 Angular Gyrus Receives the visual information from the visual area and recodes it into the auditory form, which Wernicke’s area uses to derive its meaning. Damage to the angular gyrus – leaves the person able to speak and understand but unable to read. 27 Visual cortex Receives written words as visual stimulation 28 Motor cortex The area which controls the motor cortex as it creates the pronounced word. 29 Right vs. Left Brain Left Brain Verbal Speaking writing Right Brain Recognize faces Nonverbal Spatial tasks Music & Art 30