* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download perceptionlecture5
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Visual search wikipedia , lookup
Process tracing wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Visual servoing wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Efficient coding hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
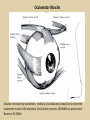
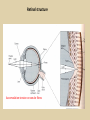
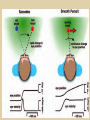
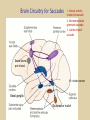
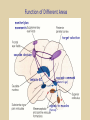
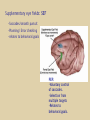
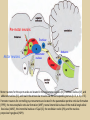
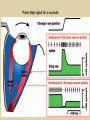
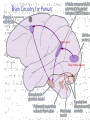
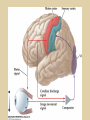
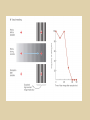
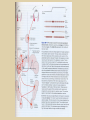
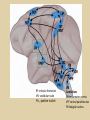
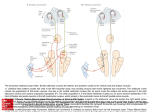
Eye movements and visual stability Kandel et al Ch 29, end of Wolfe Ch 8 Kandel Ch 39 for more info. Is a set of Reichardt detectors is sensitive to motion in one direction and only in a particular speed? It seems like an inefficient design since a great number of neurons will be required to encode motion in all possible directions and speed, unless each of them can actually encode for a small range of speed, although that might lower the sensitivity to speed change. Or the visual cortices simply have enough neurons to do so. I also want to know if information about the motion of objects stays in MT/MST etc or is it transferred to other areas to bind with other properties of objects that allow recognition of moving objects. Again the binding problem. The reason I asked the binding question again is because the integration between properties of object in the dorsal stream (eg. motion signals in MT) and properties in the ventral stream (eg. orientation and shape for object recognition) must differ somehow from integration within ventral stream for 'what' information. Referring to Campbell and Robson's experiment, the lecturer mentioned that if the cells adapt to seeing an upward motion, they will notice a "downward" motion after the motion stops. Is this the same kind of adaptation that sees an opposite color when the color disappears (like in the rotating color circle that we saw two weeks ago)? Why do we move our eyes? - Image stabilization - Information acquisition Visual Acuity matches photoreceptor density Why do we move our eyes? 1. To bring objects of interest onto high acuity region in fovea. Cone Photoreceptors are densely packed in the central fovea Why eye movements are hard to measure. A small eye rotation translates into a big change in visual angle Visual Angle x 18mm a d tan(a/2) = x/d a = 2 tan 1 x/d 1 diopter = 1/focal length in meters 0.3mm = 1 deg visual angle 55 diopters = 1/.018 Why do we move our eyes? 1. To bring objects of interest onto high acuity region in fovea. 2. Cortical magnification suggests “enhanced” processing of image in the central visual field. Oculomotor Muscles Muscles innervated by oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens (cranial) nerves from the oculomotor nuclei in the brainstem. Oculo-motor neurons: 100-600Hz vs spinal motor Neurons: 50-100Hz Types of Eye Movement Information Gathering Voluntary (attention) Stabilizing Reflexive Saccades vestibular ocular reflex (vor) new location, high velocity (700 deg/sec), body movements ballistic(?) Smooth pursuit optokinetic nystagmus (okn) object moves, velocity, slow(ish) whole field image motion Mostly 0-35 deg/sec but maybe up to100deg/sec Vergence change point of fixation in depth slow, disjunctive (eyes rotate in opposite directions) (all others are conjunctive) Note: link between accommodation and vergence Fixation: period when eye is relatively stationary between saccades. Retinal structure Accomodation:tension on zonule fibres Acuity – babies Acceleration Velocity Depth-dept gain, Precision in natural vision Ocular following - Miles otoliths Rotational (semi-circular canals) translational (otoliths) VOR Latency of vestibular-ocular reflex=10msec Demonstration of VOR and its precision – sitting vs standing It is almost impossible to hold the eyes still. Step-ramp allows separation of pursuit (slip) and saccade (displacement) Saccade latency approx 200 msec, pursuit approx 100 – smaller when there is a context that allows prediction. “main sequence”: duration = c Amplitude + b Min saccade duration approx 25 msec, max approx 200msec Demonstration of “miniature” eye movements Drift Micro-saccades Tremor Significance?? It is almost impossible to hold the eyes still. What’s involved in making a saccadic eye movement? Behavioral goal: make a sandwich Sub-goal: get peanut butter Visual search for pb: requires memory for eg color of pb or location Visual search provides saccade goal - attend to target location Plan saccade to location (sensory-motor transformation) Coordinate with hands/head Calculate velocity/position signal Execute saccade/ Brain Circuitry for Saccades 1. Neural activity related to saccade 2. Microstimulation generates saccade 3. Lesions impair saccade Dorso-lateral pre-frontal V1: striate cortex Basal ganglia Oculomotor nuclei Function of Different Areas monitor/plan movements target selection saccade decision saccade command inhibits SC (where to go) V H signals to muscles (forces) Cells in caudate signal both saccade direction and expected reward. Hikosaka et al, 2000 Monkey makes a saccade to a stimulus - some directions are rewarded. Posterior Parietal Cortex reaching Intra-Parietal Sulcus: area of multi-sensory convergence grasping LIP: Lateral Intra-parietal Area Target selection for saccades: cells fire before saccade to attended object Visual stability Supplementary eye fields: SEF -Saccades/smooth pursuit -Planning/ Error checking -relates to behavioral goals FEF: -Voluntary control of saccades. -Selection from multiple targets -Relates to behavioral goals. Pre-motor neurons Trochlear Motor neurons V Oculomotor nucleus Abducens H Motor neurons for the eye muscles are located in the oculomotor nucleus (III), trochlear nucleus (IV), and abducens nucleus (VI), and reach the extraocular muscles via the corresponding nerves (n. III, n. IV, n. VI). Premotor neurons for controlling eye movements are located in the paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF), the mesencephalic reticular formation (MRF), rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF), the interstitial nucleus of Cajal (IC), the vestibular nuclei (VN), and the nucleus prepositus hypoglossi (NPH). Pulse-Step signal for a saccade Brain areas involved in making a saccadic eye movement Behavioral goal: make a sandwich (learn how to make sandwiches) Frontal cortex. Sub-goal: get peanut butter (secondary reward signal - dopamine - basal ganglia) Visual search for pb: requires memory for eg color of pb or location (memory for visual properties - Inferotemporal cortex; activation of color - V1, V4) Visual search provides saccade goal. LIP - target selection, also FEF Plan saccade - FEF, SEF Coordinate with hands/head Execute saccade/ control time of execution: basal ganglia (substantia nigra pars reticulata, caudate) Calculate velocity/position signal oculomotor nuclei Cerebellum? Relation between saccades and attention. Saccade is always preceded by an attentional shift However, attention can be allocated covertly to the peripheral retina without a saccade. Pursuit movements also require attention. Superior colliculus Brain Circuitry for Pursuit & Supplementary Smooth pursuit Velocity signal Early motion analysis Gaze shifts: eye plus head Visual Stability Efference copy or corollary discharge Figure 8.18 The comparator Brainstem circuits for saccades. Omnipause neurons (OPN) in the nucleus raphe interpositus (RIP) tonically inhibit excitatory burst neurons (EBN) located in the paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF). When OPNs pause, the EBNs emit a burst of spikes, which activate motor neurons (MN) in the abducens nucleus (VI) innervating the lateral rectus muscle. The burst also activates interneurons (IN) which activate motor neurons on the oculomotor nucleus (III) on the opposite side, innervating the medial rectus. Inhibitory burst neurons (IBN) show a pattern of activity similar to EBNs, but provide inhibitory inputs to decrease activation in the complementary circuits and antagonist muscles. Long-lead burst neurons (LLBN) show activity long before movement onset, and provide an excitatory input to EBNs. RF reticular formation VN vestibular nucle PN , pontine nucleii Cerebellum OV oculomotor vermis VPF ventral paraflocculus FN fastigial nucleus