* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
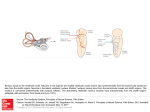
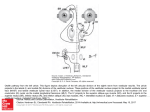
The horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex. Similar pathways connect the anterior and posterior canals to the vertical recti and oblique muscles. A. Leftward head rotation excites hair cells in the left horizontal canal, thus exciting neurons that evoke rightward eye movement. The vestibular nuclei include two populations of first-order neurons. One lies in the medial vestibular nucleus (M); its axons cross the midline and excite neurons in the right abducens nucleus and nucleus prepositus hypoglossi (P). The other population is in the lateral vestibular nucleus (L); its axons ascend ipsilaterally in the tract of Deiters and excite neurons in the left oculomotor nucleus, which project in the oculomotor nerve to the left medial rectus muscle. The right abducens has two populations of neurons. A Science, set of motor Source: nucleus The Vestibular System, Principles of Neural Fifthneurons Editon projects in the abducens nerve and excites the right lateral rectus muscle. The Citation: axons ofKandel a set ofER, interneurons cross the midline and ascend in the left medial longitudinal fasciculus to the oculomotor nucleus,2012 where they Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; Available excite the neurons at: thathttp://mhmedical.com/ project to the left medial rectus muscle. These connections facilitate the rightward horizontal eye movement that compensates for Accessed: April 29, 2017 leftward headCopyright movement. Other nuclei shown are the superior (S) and descending (D) vestibular nuclei. © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved B. During counterclockwise head movement, leftward eye movement is inhibited by sensory fibers from the left horizontal canal. These afferent fibers