* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
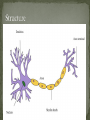
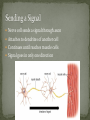
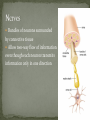
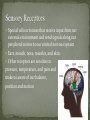
SNC 2D The organ system that is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and the peripheral nerves System that senses the environment and coordinates appropriate responses Consists of the brain and the spinal cord Shielded by bones Skull protects the brain Spine protects the spinal cord Cerebrospinal fluid surrounds the brain and spinal cord – cushions against injury and transports chemicals and waste Consists of the nerves that connect the body to the central nervous system Relays information about the internal and external environments of the brain Subdivided into A) nerves that control voluntary muscles B) nerves that carry information from sensory organs C) nerves that regulate involuntary functions Specialized cells that make up nerve tissue are called neurons Found in brain, spinal cord and nerves Approximately 100 billion neurons in human brain Neurons conduct electrical signals (nerve impulses) from one area of body to another Nerve cell sends a signal through axon Attaches to dendrites of another cell Continues until reaches muscle cells Signal goes in only one direction Fatty material that surrounds the axon Acts like an electrical wire preventing electrical impulses from passing to the wrong neuron Bundles of neurons surrounded by connective tissue Allow two-way flow of information even though each neuron transmits information only in one direction Special cells or tissues that receive input from our external environment and send signals along our peripheral nerves to our central nervous system Ears, mouth, nose, muscles, and skin Other receptors are sensitive to pressure, temperature, and pain and make us aware of our balance, position and motion Increase/decrease breathing rate Heart beat faster/slower Eat/drink/stop Perception Spinal Cord – acts as a short cut for reflexes Reflexes do not use brain, occur without conscious thought (move hand away from hot surface) Peripheral nervous system can undergo cell division to repair severed nerves (few mm distance) Central nervous system do not regenerate easily Multiple Sclerosis – destroys myelin sheaths so that signals are mixed up Fall or blow – can result in paralysis, concussions Viruses and bacteria can cause permanent damage in brain nervous system pork tapeworm