* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual
Perivascular space wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurocomputational speech processing wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Cerebral cortex wikipedia , lookup
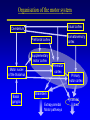
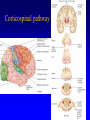
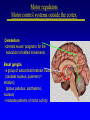
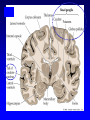
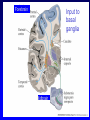
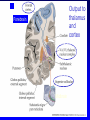
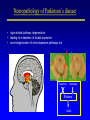
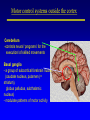
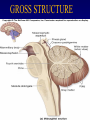
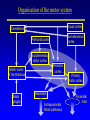
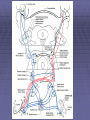
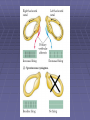
Organisation of the motor system Visual cortex Cerebellum Somatosensory cortex Prefrontal cortex Supplementary motor cortex Premotor cortex Motor nuclei of the thalamus Basal ganglia Primary motor cortex Brainstem Extrapyramidal Motor pathways Pyramidal tract Motor system includes • Tracts Corticospinal tract (Pyramidal tract ) Extra-pyramidal system • Basal Ganglia (regulator) • Cerebellum (regulator) Corticospinal pathway Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum Motor regulators Motor control systems outside the cortex Cerebellum -controls neural ‘programs’ for the executionl of skilled movements Basal ganglia - a group of subcortical forebrain nuclei (caudate nucleus, putamen (= striatum), globus palludus, subthalamic nucleus) - modulate patterns of motor activity Forebrain Input to basal ganglia Midbrain Output to thalamus and cortex Forebrain Midbrain MOVEMENT DISORDERS Parkinson disease Huntingtons disease PARKINSONS DISEASE • Effects dopaminergic neurons • Neurons are lost from substantia nigra • Rarely presents before 50 years • Neurodegenerative disease Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease • nigro-striatal pathway degeneration • leading to a depletion of striatal dopamine • some degeneration of other dopamine pathways too Dopamine Glutamate XStriatum GABA CLINICAL FEATURES Characterized by: • Tremors • Rigidity • bradykinesia Huntington’s disease • Onset of symptoms usually at 30 to 45 years • Genetically determined (single dominant gene) • Causes degeneration of the output neurones from the striatum, reducing inhibitory modulation of motor function •Progressive disease causing involuntary muscle jerks • Dopamine Glutamate Striatum X GABA HUNTINGTONS DISEASE • Inherited disorder • Autosomal dominant • Males females equally affected • Presents during the 4th decade • Chorea which worsens with time NOT Sydenham chorea • Cognitive disorders • Dementia Motor control systems outside the cortex Cerebellum -controls neural ‘programs’ for the executionl of skilled movements Basal ganglia - a group of subcortical forebrain nuclei (caudate nucleus, putamen (= striatum), globus palludus, subthalamic nucleus) - modulate patterns of motor activity GROSS STRUCTURE Organisation of the motor system Visual cortex Cerebellum Somatosensory cortex Prefrontal cortex Supplementary motor cortex Premotor cortex Motor nuclei of the thalamus Basal ganglia Brainstem Extrapyramidal Motor pathways Primary motor cortex Pyramidal tract Feed-back and feedback control circuits • Input: Cerebellar connections – Sensory cortex (somato, visual) – Vestibular system – Spinocerebellar tract • Output: – Motor cortex – Thalamus motor nuclei – Extra-pyramidal tracts The main functions of cerebellum: • body equilibrium • regulation of muscle tone • coordination of movements Ataxia • means disturbances of equilibrium of the body and coordination of movements. • Cerebellum lesion produces cerebellar ataxia Cerebellar ataxia • Attactic gait – patient can’t to walk • Disorders of equlibrium – patient can’t to stand • Intention tremor – is dynamic tremor (it is more expressed while moving and disappears while rest) • Nystagmus • Dysmetria (disturbed ability to gauge distances) Ménière Disease Disease results from a disruption of normal endolymph volume Symptoms include: Severe vertigo Positional nystagmus (nystagmus when head in a particular position) Nausea Affected individuals can also experience-unpredictable attacks of auditory & vestibular symptoms: Vomiting Tinnitus (ringing in ears) Inability to make head movements Inability to stand passively Low frequency hearing loss Treatment: administration of a diuretic (hydrochlorothiazide) & a salt restricted diet Persistent condition: shunt implantation into swollen endolymphatic sac, or delivery of a vestibulotoxic agents (gentamicin) into perilymph.