* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNA Interference
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
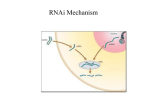
RNA Interference Hannon, Nature 418:244-251 Jacques et al, Nature 418:435-8 Carmichael Nature 418:379-380 Allshire, Science 297:1818-9 RNA Interference (RNAi) • Double stranded RNA responsible for posttranscriptional gene silencing of the gene from which it was derived. SPECIFIC • NATURAL BIOLOGICAL MECHANISM IN PLANTS, INSECTS AND MAMMALS • RNAi FUNCTIONS – regulates expression of protein coding genes – mediates resistance to both exogenous parasitic and exogenous pathogenic nucleic acid – used experimentally to block gene expression Historically Important Discoveries • 1990 – exogenous transgenes in petunias caused variegated pigmentation (Co-suppression) • Plant destruction of viral RNA; endogenous genes could be silenced if homologous sequences were present in the virus replicon • Discovered (1998) in C. elegans –dsRNA response resulting in sequence-specific gene silencing • SILENCEING – dsRNA 10x greater than (+) or (-) sense RNA • dsRNA induced gene silencing found in many euk. (Fig. 1) Why RNAi? Hypotheses and Clues Include: RNAi mechanism evolved to immobilize transposable elements and silence RNA viruses ie Mut7 -/- C. elegans; has a mutator phenotype b/c transposable element Later RNAi important in silencing chromatin – may recruit Clr4 histone H3 methylase small RNAs have been correlated w/ methylation of promoter DNA of Arabidopsis (S.pombe has no DNA methylation) both siRNAs and miRNAs regulate gene expression Exogenous and Endogenous RNAi Silencing Complex = ds siRNAi (21-23bp) Proteins* ie RISC Complexes recognize complementary ss mRNA Results in target mRNA cleavage; no protein product Experimental use of RNAi Possibly to fight viral infections??? • RNA interference can be used to posttranscriptionally silence or suppress a gene (CELLULAR or VIRAL) thru mRNA degradation; don’t need knock out mutants • RNAi testing of C. elegans ~19,000 genes! • Imagenex sells the “RNAi Gene Suppressor System” – a plasmid vector based RNAi system the allows suppression of genes in mammalian cells • sRNAi too small to induce PKR Pathway Mechanism of dsRNA Gene Silencing Dicer endonuclease enzyme dimer cleaves RNAi (RNAse III family) Small ~ 22 nucleotide RNAs assoc. w/ RISC (guide RNAs) Effector Nuclease = RISC (RNA-induced silencing complex) Latent RISC w/ ds siRNAs +ATP Active RISC w/ ss siRNAs – destroys target mRNAs Fig. 2. Hannon Review RISC –nuclease complex Precursor RISC ~ 250K Active RISC ~100K (siRNA unwinding) RISC COMPONENTS: siRNA endonuclease Drosoph. work indicates exonuclease AGO2 protein (PAZ and PIWI domains) possibly involved in shuttling of siRNAs to RISC Spreading and Amplification of Silencing Transitive RNAi – movement of silencing 3’ to 5’ along a gene RdRP – RNA directed RNA polymerase, may be involved in amplification of signal; found in tomato Arab. SDE1/SGS2 Neurosp. QDE-1 C.elegans germline EGO-1 soma – RRF-1/RDE-9 Hypoth on amplification Fig. 3 Hannon Review Genetic Studies in C. elegans RNAi silencing is heritable (unlike flies and mammals) Differential RNAi Possibly RDE-1 –4 are requirements required to deliver exogenous dsRNA to Parent Dicer requires RDE-1 –4 RDE-4 s dsRNA bind. prot. Secondarily generated both can interact w/ Dicer dsRNA synthesized from RdRP may need another protein or F1 progeny exist in a complex w/ requires MUT-7 & RDE-2 RdRP and Dicer sid-1 gene encodes Many Models/ Hypoth. transmembrane protein Fig. 5 Hannon Review – Model for the Mechanism of RNAi Modulation of HIV-1 replication by RNA interference Jean-Marc Jacque, Karine Triques & Mario Stevenson Nature Vol 418 p. 435-438 Silencing viruses with RNA G.Carmichael Introduced 22 nucleotide synthetic siRNAs (complementary to HIV target +/- GFP) into human cell lines/ primary lymphocytes RESULTS: DO NOT ACTIVATE PKR PATHWAY and siRNAs SPECIFICALLY DEGRADE HIV-1 mRNA, dsRNA-activated protein kinase PKR (RNA-dependent protein kinase) Pathway Non-specific dsRNA Response Mammalian anti-viral response; dsRNA viruses or viruses w/ dsRNA intermediates Host shut down of translation via Phosphorylation of EIF2a so that virus can not use translation machinery Genomic HIV-1 RNA in NUCLEO-PROTEIN COMPLEXES is subject to specific RNAi degradation Fig.2 HiV paper siRNAs from plasmid templates can inhibit HIV-1 Plasmid expression under T7 RNA pol. promoter of self-complementary RNA; results in dsRNA “hairpin” ALL suppressed viral production 20-30x Fig. 3 HIV Paper Science Vol. 297 Sept. 13, 2002 RNAi and Heterochromatin – a Hushed-Up Affair R. Allshire 297:1818-1819 Regulation of Heterochromatic Silencing and Histone H3 Lysine-9 Methylation by RNAi Volpe et al 297:1833-1837 Small RNAs Correspond to Centromere Heterochromatic Repeats Reinhart & Bartel 297:1831 Heterochromatin*-repetitive, condensed part of genome Post-translation modific. of histone tails important Transgenes inserted into heterochromatin are shut off SILENT CHROMATIN formed by DEACETYLATION and subsequent METHYLATION of Histone H3 Lys9 RNAi also affects silencing of gene expression TWO UNRELATED PATHWAYS??????? S. pombe (yeast) research finds that BOTH ARE PART OF THE SAME GENE-SILENCING PATH. in S. pombe repetitive DNA near centromeres is silenced via METHYLATION of H3 Lys9 and binding of Swi6 (gene express ON if Lys4 methylated) Volpe et al. found that deleting genes in RNAi pathway (argonaute, Dicer, Rdp1*) lead to LOSS of GENE SILENCING of transgenes inserted into heterochromatin RNAi and Heterochromatin Silencing are RELATED Pathways How does the RNAi machinery aid in the formation of silent chromatin? • Possibility that siRNAs bring methyltransferases to the target loci, where they are important in histone tail modification – ie. Drosoph. targets acteyltransferase w/ RNA binding chromodomain to histone H4 siRNA and Silent Chromatin - Model RNA homologous to centromeric repeats are processed – siRNAs siRNAs may recruit Clr4 histone H3 methylase result in meth. of H3 Lys9 Swi6 binds chromatin Gene silencing Related Gene Silencing Mechanisms May Function in Mammals • X chromosome inactivation in mammals – Xist RNA coating of inactive X chromosome, but no data yet suggests that Xist is processed by RNAi machinery *** • Future work using RNAi introduced in experiments should include study of chromatin structure or modifications at the locus of the affected gene • Mouse – X inactivation and Igf2r imprinting are mediated by noncoding antisense RNA • Possibly in organisms w/ DNA methylation; Histone protein modification similar to S. pombe would in turn cause DNA methylation and subsequent gene silencing regulation FOR MORE INFO. ON CORRELATION SEE Volpe et al. SCI 297:1833-1837 Jenuwein, T Science 297:2215-2218