* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurons - Jordan High School
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
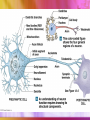
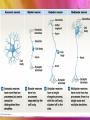
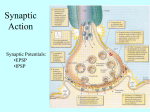
Neurons vs. neuroglia Anatomical Divisions of Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) Spinal cord & brain Integrate, process, coordinate data Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Neural tissue outside CNS Delivers sensory info, carries motor commands Nerves vs. cranial nerves vs. spinal nerves Functional Divisions of PNS Afferent division Brings sensory info to CNS from receptors Efferent division Carries motor commands from CNS to target organs (effectors) Somatic nervous system vs. autonomic nervous system Structure of Neurons Cell body Perikaryon contains organelles & neurotransmitters Dendrites vs. axons Axon: axon hillock telodendria synaptic terminals Synapse Presynaptic cell synaptic cleft postsynaptic cell Presynaptic cell releases neurotransmitters Classification of Neurons Anaxonic vs. bipolar vs. unipolar vs. multipolar neurons Sensory vs. motor vs. interneurons Sensory = afferent, motor = efferent Intero-, extero- & proprioceptors Interneurons most abundant Neuroglia of CNS Ependymal cells Line passages for cerebrospinal fluid Astrocytes Maintain blood-brain barrier Oligodendrocytes From myelin sheaths around axon Microglia Remove cell debris Neuroglia of PNS Satellite cells Surround cell bodies Schwann cells Form sheath around axons Resting Potential ↑Na+ & Cl- in extracellular fluid (ECF), ↑ K+ in intracellular fluid (ICF) Neuron interior negative compared to outside Electrochemical gradient for K+ ICF conc. ↑, ECF conc. ↓ (chemical gradient) Electrical gradient opposes K+ movement; small amounts of K+ move into ECF Electrochemical gradient for Na+ ICF conc. ↓, ECF conc. ↑ Electrical gradient draws Na+ into cell Read Table 12-1!! Na+ & K+ channels Passive channels always open Chemically gated channels need specific chemicals Voltage-gated channels respond to changes in transmembrane potential At resting potential, most gated channels closed Graded Potentials Na+ enters cell, transmembrane potential becomes more positive (depolarization) More open channels = more Na+ = more depolarization Repolarization vs. hyperpolarization Action Potential (Nerve Impulse) All-or-none principle Action potential begins between -60 & -55 mV (threshold) Stimulus triggers action potential, or not at all if doesn’t meet threshold Examine Figure 12-14 (pg 396-397) for steps of action potential Saltatory propagation—impulse jumps from node to node, impulse travels quicker Larger axon diameter = lower resistance Type A fibers—largest myelinated, fastest impulse speed Type B fibers—smaller myelinated, medium impulse speed Type C fibers—smallest & unmyelinated, slowest impulse speed Electrical vs. chemical synapses Most synapses are chemical Excitatory neurotransmitters vs. inhibitory neurotransmitters Cholinergic synapses release ACh ACh releases into synaptic cleft ACh causes depolarization of postsynaptic membrane Postsynaptic Potentials Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) Depolarization of postsynaptic membrane Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) Hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane Temporal vs. spatial summation EPSPs & IPSPs balance polarization