* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download E3R Game 1 Order That Student Copy
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
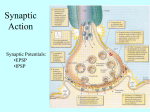
Human Biology Biology 105-55244 Review Game Students must place the following activities in the correct chronological order: Transmission across a Synaptic Cleft: A. Receptors are ligand gated sodium ion channels which allow Na+ to enter the postsynaptic neuron (or muscle) and triggers an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron (or muscle contraction) B. Action potential gets to the end of the presynaptic axon C. The Ca++ triggers synaptic vesicles located at the axon terminal to merge with the neural membrane D. Neurotransmitters travel across the synaptic cleft to the postsynaptic neuron (or the muscle) E. Neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron (or muscle) F. Once the neurotransmitters are released they need to be destroyed or contained quickly G. Synaptic vesicles release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft H. Action potential triggers Ca++ to enter the presynaptic axon terminal STEP 1: __________ STEP 2: __________ STEP 3: __________ STEP 4: __________ STEP 5: __________ STEP 6: __________ STEP 7: __________ STEP 8: __________ Human Biology Biology 105-55244 Review Game Students must place the following activities in the correct chronological order: Muscle Contraction A. The sarcoplasmic reticulum releases Ca++ B. The receptors are ion channels that open C. An action potential travels through the T tubules D. Opens binding site for the myosin to attach E. Myosin slides past the actin F. Neurotransmitters are released G. The Ca++ binds to the troponin on the actin filament H. Neurotransmitters bind to the receptor on the sarcolemma I. Myosin binds to the actin J. The action potential goes to the sarcoplasmic reticulum K. Action potentials are transmitted through the neurons STEP 1: __________ STEP 2: __________ STEP 3: __________ STEP 4: __________ STEP 5: __________ STEP 6: __________ STEP 7: __________ STEP 8: __________ STEP 9: __________ STEP 10: __________ STEP 11: __________ Human Biology Biology 105-55244 Review Game Students must place the following activities in the correct chronological order: Coagulation A. Platelets adhere to the damaged site B. Clotting factors activate inactive proteins in a cascade C. Fibrin strands form and trap blood cells and Platelets form a meshwork forming a clot and sealing the damaged vessel D. Blood vessel damage occurs E. Clotting factors are released at the site of the injury F. Clot contracts and pulls damaged edges together G. Blood vessel constricts/spasms STEP 1: __________ STEP 2: __________ STEP 3: __________ STEP 4: __________ STEP 5: __________ STEP 6: __________ STEP 7: __________