* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System: Overview
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
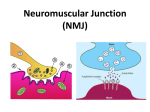
Neuromuscular Junctions To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Support and Movement Activity: Animations Title: Neuromuscular Junctions Introduction 1. Voluntary muscles are controlled by the brain. Describe this neural connection. An action potential starts from the brain to signal skeletal muscle contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. Components of the NMJ 2. Identify each of the following: Motor neuron Synaptic end bulb Sarcolemma Skeletal Muscle Cell Synaptic Cleft 3. a. Define a neuromuscular junction. A chemical synapse between the motor neuron membrane (synaptic end bulb) and the muscle membrane (sarcolemma). b. Define a synaptic cleft. Physical space that separates the two cell membranes. c. What is the function of acetylcholine? Neurotransmitter chemical that carries the information from the muscle cell to the neuron across the synaptic cleft. . Neurotransmission and the NMJ 4. What affect does depolarization have on the motor end plate once action potentials arrive at the synaptic end bulb? This change in voltage opens voltage-gated calcium channels allowing calcium to flood into the neuron. 5. What is the affect of increased calcium within the neuron? Causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the neuron membrane, and acetylcholine is then released into the synaptic cleft. 6. What affect does acetylcholine have on the sarcolemma? It triggers the opening of sodium channels resulting in the rapid entry of sodium into the muscle cell. 7. What affect do increased sodium ions have on the muscle cell? It depolarizes the sarcolemma and generates a muscle action potential that travels along the membrane. . Initiation of Contraction 8. Once an action potential goes down a T-tubule, what affect does it have on the terminal cisterns of the sarcoplasmic reticulum? It causes changes in the terminal cisterns of the SR. 9. What is the function of the ligand-gates calcium channels? Releases calcium ions into the cytosol. 10. a. Define a sarcomere. It is the smallest contractile unit where contractile proteins are organized in a specific arrangement. a b. Identify the actin and myosin filaments. c. What is the role of troponin and tropomyosin? Durjng periods of rest, troponin blocks the actin binding sites on tropomyosin and prevent the filaments from attaching (and, therefore, the entire cell from contracting). d. What affect does calcium have on troponin and tropomyosin? How does this affect the muscle? Calcium binds to the troponin complex and changes its shape. This uncovers the actin binding sites on troponin and allows myosin heads to bind to actin which initiates sarcomere contraction.. Relaxation 11. a. What is the function of acetylcholinesterase? This enzyme breaks down acetylcholine and prevents the generation of multiple muscle action potentials from a single nerve impulse. Another muscle action potential will only occur when a new neuron action potential causes the release of more acetylcholine. b. How do declining acetylcholine levels affect the muscle? Decreasing levels of acetylcholine will prevent the generation of another muscle action potential. c. What happens to the calcium ions that were released from the terminal cisterns? Pumped back into the SR and stored until another action potential occurs. d. How does removal of the calcium ions affect the filaments? Troponin complex will return to its normal configuration and cover the actin binding site on tropomyosin thus preventing further interaction between the actin and myosin filaments, and contraction ends.