* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
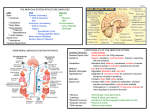
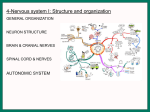
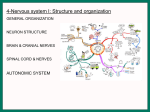
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System Receive Sensory Input Integrate Information (Immediate response, ignore it, store in memory) Control Muscles and Glands Maintain Homeostasis Mental Activity Divisions of the Nervous System 2 major divisions of the nervous system Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerves and ganglia outside of the CNS 31 pairs of spinal nerves and 12 cranial nerves Functional Subdivisions of the PNS Sensory division: (Afferent) PNSCNS Motor division: (Efferent) CNS Muscles and Glands CNS vs PNS Somatic Motor Nervous System and Autonomic Nervous System Somatic Motor Nervous System Voluntary and reflexes Autonomic Nervous system Involuntary Sympathetic Division ( prepares the body for physical activity) Parasympathetic Division (Activates functions of the body while at rest goes back to normal) CNS PNS Brain & Spinal Cord Cranial & Spinal Nerves Sensory Division Motor Division (Periphery → CNS) (CNS → Periphery) Afferent/Incoming Efferent/Outgoing Cranial Spinal Nerves Nerves Somatic Motor NS Autonomic NS Voluntary Involuntary (Reflexes) Sympathetic Stimulatory Parasympathetic Inhibitory GI Enteric Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” which conducts impulse away from the cell body, sends information (Action Potentials) Types of Neurons Unipolar: 1 process, a neuron with a single axon (Sensory, afferent neurons) Bipolar: 2 process, one dendrite and one axon (Special senses, retinal, nasal cavity) Multipolar: Several dendrites and one axon (CNS and all motor efferent) Neuroglia 5 types of Neuroglia Astrocytes: CNS structural support, create the blood brain barrier, and tissue repair. Ependymal: Produce and help circulate cerebrospinal fluid. Microglia: Fights infection, and help remove bacteria and cell debris. Oligodendrocytes: Found in the CNS and insulation around axons. Schwann Cells: Found in the PNS and insulation around axons. Neuroglia Neuroglia Schwann Cells Myelinated Axons Myelinated Axon: Conducts at a faster rate. Allows the action potential to jump from nodes of Ranvier. White vs. Grey Matter Myelinated (white matter) – myelinated axons Unmyelinated (grey matter) - unmyelinated