* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Broca's area wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
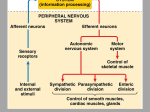
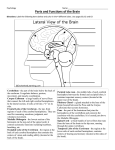
SI Bio6 Dr. Wright’s class made by Pyeongsug Kim Revised: 03/16/10 Chap 8. Central Nervous System 1. (I know this questions are for chapter 7 problems, I have forgotten to put in Chapter 7 practice questions). Now indicate whether the following events would stimulate or inhibit skeletal muscle activity. stimulate Acetylcholine binds nicotinic receptors on the muscle cell membrane. inhibit Calcium is blocked from entering the axon end plate in the presynaptic neuron. stimulate Acetylcholine stays in the synaptic cleft for too long. stimulate Reuptake pump in presynaptic neuron is inhibited. inhibit Sodium channels in the muscle cell membrane are blocked and cannot open stimulate Potassium channels in the muscle cell membrane are blocked and cannot open inhibit The medication similar to Acetylcholinsterase is taken. 2. Match the term. The answer may be more than one. cerebrum The postcentral gyrus is located here. midbrain diencephalon The subtantia nigra projects from here to the basal nuclei. The thalamus and hypothalamus are located here. medulla oblongata Breathing and heart rate are controlled from the region. cerebrum cerebrum The precentral gyrus is located here. The basal nuclei are located deep within this region of the brain. pons The peneumotoxic and apneustic centers are located within this region. cerebrum Temporal lobe and frontal lobe are located here. cerebrum The corpus callosum connects the two hemispheres that define this region. Name two parts of the brain (from the list below) that contribute to motor control cerebrum, cerebellum cerebrum, diencephalon diencephalon epithalamus. Pons, medulla oblongata a. cerebrum Name two parts of the brain (from the list below) that contain part of the limbic system. is the region of the brain that includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, and b. Cerebellum Is(are) located in the brain stem c. diencephalon d. midbrain e. pons f. medulla oblongata 3. Match the term.(choose the best the answer) hypothalamus medulla oblongata Regulate hunger and thirst, body temperature, and emotions contains grouping of neurons that control heart function and some aspects of breathing. medulla oblongata controls the activity of ANS system (sympathetic, parasympathetic). corpus callosum connects the two hemispheres thalamus part of the diencephalons, it relays sensory information to the cerebrum. amygdale Part of the limbic system, this contributes to the feeling of fear. RAS group of neurons associated with sleepiness and wakefulness. Also known as corticospinal tracts, these convey motor output directly to the spinal pyramids midbrain cord. The nigrostriatal system is located here. SI Bio6 Dr. Wright’s class cerebellum basal nuclei hypothalamus made by Pyeongsug Kim Revised: 03/16/10 helps coordinate movement by sending inhibitory signals to various parts of the brain. Gray matter deep within the cerebrum; Various effects on voluntary movement. integrates nervous and endocrine systems, in other words Autonomic and endocrine responses are coordinated here; Regulates pituitary. a. amygdale(amygdale), b. thalamus, c. hypothalamus, g.medulla oblongata, i. corpus callosum, j. cerebellum d. pyramids e. midbrain k. basal nuclei f. RAS, 3. a. Name two region in brain have centers that help regulate breathing. Pons, medulla oblongata b. Name the region in the brain where all sensory except one sensory information pass through. What is the exception of sensory? Thalamus; smell c. Name two region of the body have a lot of sensory and motor neurons. Hands and face d. Name a region of the body have not as many sensory and motor neurons even though it is a much larger body area. Trunk 3. Match the term.(choose the best answer) cerebrum, The sensorimotor cortex is located here. medulla oblongata thalamus cerebellum cerebral cortex limbic system Regulation digestive function and heart rate. All sensory information except smell passes through this, on the way to the cerebrum. Required for motor learning, coordination and storage of trained physical activity; communicates with the cerebrum through the thalamus. Regulate sensory info and motor response. The general name for several structures involved in developing “survival” behaviors such as aggression, fear, sex drive, reward and punishment. cerebrum Broca’s area The basal nuclei are located deep within this region. Wernicke’s area Involves speech comprehension. Involves motor coordination of speech. a. limbic system, b. Wernicke’s area g. cerebral cortex h. Broca’s area c. thalamus, d. cerebrum, e.medulla oblongata f. cerebellum a. Name two regions; damage to either causes an aphasia. Wernicke’s area, Broca’s area 4. Match the brain lobe and each function. Insula memory, pain response, stress response beneath and overlapping other lobes Temporal lobe hearing Parietal lobe Frontal lobe sensory and motor interpretation, speech, spatial interpretation voluntary control of skeletal muscles, higher intellectual function verbal function. Occipital lobe vision a. Frontal lobe b. Parietal lobe c. Temporal lobe d. Occipital lobe e. Insula SI Bio6 Dr. Wright’s class 5. Match the term to definition. thalamus made by Pyeongsug Kim Revised: 03/16/10 Acts primarily as a relay center (and filter) for sensory information. Loss of the ability to coordinate muscular movement.(may be due to damage in Ataxia cerebellum) The component of the limbic system is associated with consolidation of short-term Hippocampus and long-term memory. RAS A system in the brain associated with wakefulness. This region receives input from the eyes, vestibular apparatus and cerebellum to vestibular nuclei help coordinate a sense of equilibrium. Pineal gland This structure secrets melatonin. amygdale(amygdale) This region is important for memory of fear responses. medulla oblongata Rhythmicity of breathing is regulated here. Aphasia Describes the loss of speech a. Hippocampus b. thalamus g. vestibular nuclei c. amygdale(amygdale), h. medulla oblongata d.RAS e. Pineal gland f. Aphasia i. Ataxia *The vestibular nuclei are the cranial nuclei for the vestibular nerve. 6. Match the brain region when disorder occurs. Substantia Parkin’s disease Broca’s area Loss of ability to physically form words cerebellum Loss of coordination; inability to reach for an object without overshooting. hypothalamus Inability to develop a sense of satiety, thirst. amygdale(amygdale), Loss of rational sense of fear. RAS Loss of general sense of consciousness or wakefulness medulla oblongata Inability of autonomously control heart rate. Wernicke’s area Can say words but cannot speak in a comprehensible manner. Broca’s area Comprehension good; Speech is slow and difficult. a. Broca’s area b. hypothalamus c. amygdale(amygdale), f. cerebellum g. Substantia h. medulla oblongata d.RAS e. Wernicke’s area