* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Memory - My Haiku
Spatial memory wikipedia , lookup
Autobiographical memory wikipedia , lookup
Fuzzy-trace theory wikipedia , lookup
Remember versus know judgements wikipedia , lookup
Effects of stress on memory wikipedia , lookup
Transsaccadic memory wikipedia , lookup
Visual memory wikipedia , lookup
Procedural memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory error wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Implicit memory wikipedia , lookup
Multiple trace theory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Art of memory wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Effects of alcohol on memory wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive memory wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Encoding (memory) wikipedia , lookup
Collective memory wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
Episodic-like memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
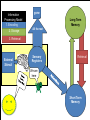
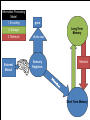
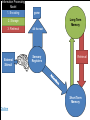
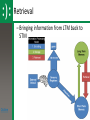
Unit 3: Memory Warm Up Are you (or someone you know) able to seemingly quote a whole movie or sing any song from memory? How do you think that’s possible? AP Psychology Unit 3: Memory (Cognition) Essential Task 3-1: Describe the information processing model of memory with specific attention to the following steps: - Encoding: external stimuli, sensory registers, selective attention, reticular formation, short-term memory - Storage: long-term memory, explicit memory (semantic and episodic memories) and implicit memories (emotional and procedural memories) - Retrieval Information Processing Model 1. Encoding 2. Storage gone Long Term Memory All the rest 3. Retrieval External Stimuli Sensory Registers Retrieval We are here Short Term Memory Essential Task 3-1: Outline • Define memory • Describe the Information Processing Model or IPM for short – Encoding: • • • • external stimuli sensory registers selective attention short-term memory – Storage: • long-term memory, – explicit memory (semantic and episodic memories) – implicit memories (emotional and procedural memories) – Retrieval Memory • The ability to remember things we have experienced, imagined, or learned • Memory is often seen as steps in an information-processing model Outline Information Processing Model – Encoding – (The process of putting information into digital format.) – Storage – Hard Drive – Retrieval – Accessing the Hard Drive Outline Information Processing Model 1. Encoding gone Long Term Memory 2. Storage 3. Retrieval External Stimuli All the rest Sensory Registers Retrieval Short Term Memory Seven Dwarves Activity Outline Recognition is easier than recall • Grouchy, Gabby, Fearful, Sleepy, Smiley, Jumpy, Hopeful, Shy, Droopy, Dopey, Sniffy, Wishful, Puffy, Dumpy, Sneezy, Lazy, Pop, Grumpy, Bashful, Cheerful, Teach, Shorty, Nifty, Happy, Doc, Wheezy, and Stubby. Outline Information Processing Model 1. Encoding gone Long Term Memory 2. Storage 3. Retrieval External Stimuli All the rest Sensory Registers Retrieval Short Term Memory Outline Sensory registers • Sensory registers are the first stop for all sensory information • The sensory registers are very large, but information stays for only a very short time Outline Visual and Auditory Registers • Visual register holds images, or icons, that represent all aspects of a visual image – Icons normally last about ¼ second in the visual register • Auditory register holds echoes of sound – Echoes can last up to several seconds in the auditory register Outline • Why do the auditory registers last longer? Now let us test your visual registers • I will flash the next picture for just ¼ of a second. • DON’T BLINK • After the image flashes we’ll return to a white screen and you can tell me everything you saw. Outline Outline Did you pay attention to everything? Outline Here is another image • DON’T BLINK Outline Outline How big is your attention? Outline Selective Attention • Selects certain information for further processing • We normally pay attention to only a SMALL (PLEASE ENJOY THE IRONIC FONT SELECTION) of incoming information Outline portion Short-term Memory (STM) • Short-term memory holds information we are aware of or thinking about at any given moment • Sometimes referred to as working memory Outline Capacity of Short-Term Memory • Research indicates that STM can hold 7+/- 2 bits of information • Larger amounts of information can be held by using the process of chunking Outline Encoding • Information can be stored: • Phonologically (according to how it sounds) • Visually • visually encoded info > phonologically encoded info Outline Let’s see how good your STM is! Outline Short Term Memory Outline • • • • • • • • 9754 68259 913825 5963827 86951372 719384273 9152438162 15284673189 Chunking Helps Outline • • • • • • • • • 97-54 6 8 -2 5 9 9 1 -3 8- 2 5 5 9 -6 3- 8 2 7 8 6 9- 5 1 3- 7 2 7 1 9 -3 8 4- 2 7 3 9 1 5 -2 4 3- 8 1- 6 2 1 5 2 8 -4 6 7 3- 1 8 9 Think of the concept maps – creates chunks Maintaining STMLTM • Information can be held in STM by using rote rehearsal, also called maintenance rehearsal • Rote rehearsal: repeating information over and over – not very effective if no intent to learn Outline Long-term Memory • Everything that is learned is stored in long-term memory • Capacity of long-term memory: – Vast amounts of information may be stored for many years – No known limits to its capacity Outline Encoding in Long-term Memory • Most information is encoded in terms of meaning • Some information: Outline – is stored verbatim – is coded in terms of nonverbal images – Research has shown that memory for visually encoded information is better than phonologically encoded information CONCEPT MAPS CREATE A VISUAL!!!! Maintaining LTM Elaborative rehearsal • Process of relating new information to information already stored in memory Schema/Schemata A schema is a set of beliefs or expectations about something based on past experience • Incoming information is fit into existing schemata E.g, House • House, cottage mansion, cabin, manor, poorhouse, duplex, apartment Types of Long Term Memory • Explicit memory – Episodic Memory – Semantic Memory • Implicit memory – Procedural Memory @#$!& @#$!& Outline – Emotional Memory Types of Long Term Memory • Explicit memory – Memory for information we can readily express and are aware of having – This information can be intentionally recalled – Episodic Memories - Memories for personal events in a specific time and place – Semantic Memories - Memory for general facts and concepts not linked to a specific time Outline Types of Long Term Memory • Implicit memory – Memory for information that we cannot readily express and may not be aware of having – Cannot be intentionally retrieved – Procedural memories: Motor skills and habits – Emotional memories: Learned emotional responses to various stimuli Outline Retrieval – Bringing information from LTM back to STM Outline Elaborative Rehearsal! For the following, explain in your own words and give a personal example (3+ sentences) of each: 1. Explicit Memory 2. Implicit Memory 3. Episodic Memory 4. Semantic Memory 5. Procedural Memory 6. Emotional Memory 7. Selective Attention 8. Describe a time that you used rote rehearsal. -Why did you need to use rote rehearsal? -Was it effective? Why/why not? -Would you be able to retrieve that information from your LTM? Why/why not? 9. Schemata Describe your schema regarding equality: What are your set of beliefs surrounding the idea of equality. • Once you’ve described your schema, explain how the following fit into your schema: • Gender, Race, Religion, Sexuality, Handicap, Socioeconomic status, Gender Identity (Intersex, Transgender)