* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain, Body, and Behavior
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
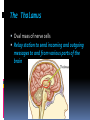
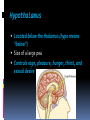
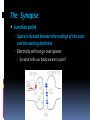
Chapter 3 BRAIN, BODY, AND BEHAVIOR Examining the Brain Study the brain in detail because it is the part of us that controls every thought, action, and feeling The Brain uses 20% of all our oxygen, eats up most sugar we take in, and is made up of about 100 billion nerve cells The Cerebral Cortex Outermost layer of the brain High level of thinking occurs in this area If the cortex were untwisted and spread out it is about the size of a large bath towel The Hemispheres Halves The brain is divided into two halves A fissure is what separates the two halves Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body The corpus callosum helps each half of the brain communicate with the other half The Lobes The Cerebral Cortex is divided into four major sections called Lobes Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe The Lobes Frontal Lobe Foremost area The motor strip is located in the frontal lobe This allows movement of the body Parietal Lobe Located behind the Frontal Lobe Sensory strip is located here Allows a person to feel sensations The Lobes Occipital Lobe Very back of the brain Devoted to making sense out of what we see The brain sits in a fluid that acts like a shock absorber so the brain can move back and forth Temporal Lobe Bottom of the brain Major centers for hearing The Frontal Lobe Prefrontal Area Located behind your forehead Allows us to re-experience past events Frontal Association Area Heavily packed with nerve cells Phineas Gage Railroad worker Experienced damage to his frontal association area and changed drastically Hemispheres and Handedness When dealing with small, fine movements, such as writing one hemisphere will have dominance The intelligence of right versus left handed people is about the same Myths: If a left handed child is forced to use their right hand they may become insane Parents would sometimes make their children switch to using their right hands Tasks of the Cerebral Hemispheres Left Hemisphere handles verbal or speech material The right hemisphere deals with objects in space, art, music, and some mathematical reasoning Both hemispheres work together in virtually everything we do The Lower Brain The lower brain is located deep inside the skull with the cerebral cortex fitting over and around it Cortex means “bark” as on a tree Bark protects a tree just like the cortex protects our lower brain The Thalamus Oval mass of nerve cells Relay station to send incoming and outgoing messages to and from various parts of the brain Hypothalamus Located below the thalamus (hypo means “below”) Size of a large pea Controls rage, pleasure, hunger, thirst, and sexual desire The Limbic System Contains structures involved in basic emotions and to some extent memory 2 Structures are important in the limbic system Amygdala – responsible for emotional responses especially aggression Hippocampus – allows us to form memories Memories are not stored in the hippocampus If the hippocampus is damaged new memories cannot be formed The Cerebellum Looks like a ball of yarn a little larger than a golf ball Complex Balance, coordination, gets you where you need to go First day of school you followed your schedule but within a week you no longer had to “pay attention” - you magically arrived The Reticular Activating System (RAS) Sits at the base of the brain inside of the spinal cord Reticular means “net” and the RAS catches nerve impulses Regulates alertness and sleepiness Sensitive to steady sounds Major blow to the head may cause the RAS to shut down Change in rhythm can stir up the RAS Brain Communication All parts of our brain has to communicate with one another as well as our body We need nerve cells that are separate but able to alternate signals from one circuit to another The Neuron Each nerve cell is separate from the others The body of the neuron has fibers sticking out from it Short fibers are called dendrites Look like branches Axons carry the message from the cell to other neurons Thousands of terminals that sit opposite a receptor for another neuron Message comes to a receptor on a dendrite, goes through the cell and then goes out the cell’s axon to another neuron The Synapse Junction point Space is located between the endings of the axon and the waiting dendrites Electricity will not go over spaces So what tells our body we are in pain? Neurotransmitters Chemical “messengers” deliver messages to across the synapse Different molecules have different shapes and make-ups Acetylcholine regulates your body’s movement and memory Dopamine – shortage of this is a main role in Parkinson’s Disease Endorphins – made by the body and is a natural form of morphine The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Central Nervous System Brain and Spinal Cord All nerve impulses must enter and exit by the spinal cord In an emergency the spinal cord reacts before the brain does The spinal cord has very few synapses to slow down messages The Peripheral Nervous System Everything minus the brain and spinal cord Somatic Nervous System Composed of sensory and motor nerves The Autonomic System Controls the things we do automatically Breathe, digest food, pupil dilating, heart Can be overridden by the brain The Endocrine System The Pituitary Gland Master gland of the body – bean shaped unit that is attached and controlled by the hypothalamus 2 jobs Send messages that will start other glands going Determine how tall or short we will be When things are not working properly incredible growth can occur Poor nutrition can also affect your growth The Endocrine System The Thyroid Gland Sits inside the neck Controls metabolism Overactive Thyroid Can result in restlessness, nervousness, and anxiety Underactive Thyroid Can result in a sad mood, or even depression The Endocrine System Adrenal Glands Pump adrenaline into the bloodstream Adrenaline prepares us for emergencies Even sends out a chemical that will help the blood clot faster incase we are cut Do not have to be in an emergency for the adrenal glands to start working Important tests, talking to a judging audience Right Brain vs Left Brain Which are you the most? Do you agree or disagree with the description? Why or why not? Use two examples that prove or disprove the summaries?