* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PSYCH-UNIT-2-0 -NOTES-BIO-INTRO
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Phineas Gage wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
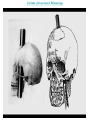
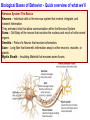
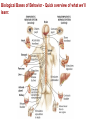
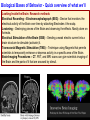
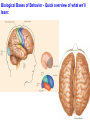
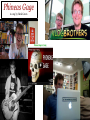
The curious case of Phineas Gage Neuroscience's Most Famous Patient Psychology Unit 2 - Biological Bases of Behavior YouTube: The Unfixed Brain YouTube: Curious Case of Phineas Gage Phineas P. Gage (1823-1860) American railroad construction worker. ★ He is remembered for his improbable survival of an accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head. ★ Much of his left frontal lobe was destroyed. ★ The reported effects were personality & behaviorally based. ★ Over the succeeding 12 years - effects so profound that for a time (at least) his friends reported that they say him as, “No longer Gage.” The Curious Case of Phineas Gage ★ Personality comes from the brain, not heart. ★ We can operate on the brain and people could survive. ★ Very famous example in medical & psychological research. YouTube: NOVA Now - Phineas Gage Biological Bases of Behavior - Things to Know 1. The different methods for peering into the human brain 2. What the areas of the brain control 3. The structure of the neuron 4. The action potential 5. The role of neurotransmitters in neural transmission Biological Bases of Behavior - Quick overview of what we’ll learn: Nervous System: The Basics Neurons – Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. They are basic links that allow communication within the Nervous System. Soma – Cell Body of the neuron that contains the nucleus and much of cells normal organs. Dendrite – Parts of a Neuron that receives information. Axon – Long fiber that transmits information away to other neurons, muscles, or glands. Myelin Sheath – Insulating Material that encases some Axons. Biological Bases of Behavior - Quick overview of what we’ll learn: Organization of Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System & Central Nervous System Nerves – Bundles of Neuron Fibers (Axons) that are routed together in the Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System – Made up of all those nerves that lie outside the Brain and Spinal Cord. Somatic Nervous System – Made up of Nerves that connect to voluntary skeletal Muscles and to Sensory Receptors. Biological Bases of Behavior - Quick overview of what we’ll learn: Biological Bases of Behavior - Quick overview of what we’ll learn: Looking Inside the Brain: Research methods Electrical Recording – Electroencephalograph (EEG) - Device that monitors the electrical activity of the Brain over time by attaching Electrodes t the scalp. Lesioning – Destroying pieces of the Brain and observing the effects. Mostly done on Animals. Electrical Stimulation of the Brain (ESB) – Sending a weak electric current into a brain structure to stimulate (activate) it. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) – Technique using Magnets that permits scientists to temporarily enhance or depress activity in a specific area of the Brain. Brain-Imaging Procedures – CT. PET, and MRI scans can give scientists imaging of the Brain and the parts of it that are aroused by stimuli. Biological Bases of Behavior - Quick overview of what we’ll learn: Biological Bases of Behavior - Quick overview of what we’ll learn: Biological Bases of Behavior - Quick overview of what we’ll learn: Endocrine System ★ Endocrine System – Consists of Glands that secrete chemicals into the bloodstream that help control bodily functioning. ★ Hormones – The chemical Messengers in the Endocrine System. ○ Hormones travel throughout the body much slower than Neurotransmitters. ○ They regulate many physical and Behavioral functions. ★ Pituitary Gland – Based in the Hypothalamus, it releases the Hormones into the body. ★ The Endocrine System is in charge of the Adrenaline effect. Biological Bases of Behavior - Quick overview of what we’ll learn: Heredity and Behavior Behavioral Genetics – Field that studies the influence of Genetic Factors on Behavioral Traits. Basic Principles of Genetics Chromosomes – Strands of DNA that carry Genetic Information. Zygote – Single Cell formed by the union of a Sperm and Egg. Genes – DNA segments that serve as key units in Hereditary Transmission. Some video clips to get your brain going... LITERALLY. Phineas Gage A song by Hank Green YouTube: Hank Green - Phineas Gage ~ A Song YouTube: Psychology 101 - Biological Bases of Behavior - Introduction YouTube: Psychology 101 - Biological Bases of Behavior - Parts of the Brain YouTube: Psychology 101 - Neuroplasticity