* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Central Nervous System
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
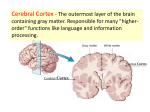
Central Nervous System Part 1 Glial Cells and CSF Brainstem, Cerebellum and Diencephalon Fig. 49-6a Glial Cell Types: Most of the brain is made up of cells that support the nervous tissue CNS VENTRICLE Ependymal cell PNS Neuron Astrocyte Oligodendrocyte Schwann cells Microglial cell Capillary (a) Glia in vertebrates _________________________ produces myelin sheath _________________________: maintains environment for nerve impulses, blood brain barrier, provides nutrients, picks up excess NT ________________________: WBC of the brain ________________________: lines ventricles and makes CSF Protection: Skull, Meninges and CSF: ~ 150 mL CSF in ventricles and subarachnoid space • ______________________ • ______________________ • ______________________ • CSF Circulation: lateral > interventricular foramen > 3rd > cerebral aqueduct > 4th • Superior sagital sinus and arachnoid villi • Capillaries are different: _______________________ _______________________ __________________: specialized capillary network projecting from the _______________ into the ventricles of the brain forming cerebral spinal fluid (70% of CSF) 99% water, (glucose, aa, salt, less density and protein than plasma) Fig. 49-9c Cerebrum (includes cerebral cortex, white matter, basal nuclei) Diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus) Midbrain (part of brainstem) Pons (part of brainstem), cerebellum Medulla oblongata (part of brainstem) Diencephalon: Cerebrum Hypothalamus Thalamus Pineal gland (part of epithalamus) Brainstem: Midbrain Pons Pituitary gland Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Cerebellum Central canal (c) Adult BRAINSTEM: ____________, _______________,____________ ___________________________; w/ pyramidal tracts, • * CV & Vasomotor center VITAL CENTERS •top of the spine, two bulges of white matter = pyramids (pyramid tracts) •All ascending sensory and descending motor tracts VITAL CENTERS (CV and Vasomotor center) Cardiovascular center (rate/force of heart) diameter = _______________ Respiratory center: adjust basic rhythm of breathing Reflex: vomit, cough, sneeze, swallow Reticular formation: gray matter from spine to thalamus Keeps _______________________________________ Reflex centers: ____________________________________________ 12 pairs of cranial nerves _______ w/ Reticular formation is a relay pathway between the motor cortex and the cerebellum also functions as a *pneumotaxic center *houses cranial nerves: trigeminal, abducens, and facial. Respiration center Reflex w cranial nerves 5-8, eye, chewing, facial expression, taste, equilibrium _________________ w/ cerebral peduncles ___________________: Righting reflexes Superior colliculi: visual reflex center Inferior colliculi: auditory reflex center ______________________: pigmented neurons in motor fxn and produces the precursor for the neurotransmitter ______________ __________________ (pink)important for acting as a relay between motor cortex and muscles of the limbs for limb flexion; III. CEREBELLUM ______________: coordination of skeletal muscle movements Some cognitive function in predicting motor movements Fine coordination: 3 main functions ____________________________________ ____________________________________ Flocculonodular lobe= _________________________ Hemispheres separated by falx cerebelli Cerebellar cortex – gray But mainly white matter underneath : __________ 30 million purkinje cells in cerebellar cortex integrate info motor activity to keep informed about ____________________ axons carry info to nuclei for relay to brainstem DIENCEPHALON • • • • • • • • Thalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Mammillary bodies Epithalamus Choroid plexus Reticular formation RAS ________________ : all sensory except smell to the cerebrum expresses emotions with hypothalamus cognition: awareness and acquisition of knowledge Hypothalamus w/ VITAL CENTERS: •maintain and regulate _____________________ •sleep and wake patterns controls __________________ •link the endocrine and nervous systems •secretes variety of hormones that regulate pituitary secretes __________ and ______________________ •__________________ (thirst) •__________________ •__________________ •sexual behavior and emotional aspect of sensory Pituitary gland: ____________________ of the body secretes: • ____________: secretes oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone; anterior lobe: •ACTH affects adrenal cortex; TSH affect thyroid and thyroxin; FSH,LH affects ovary and testes; •____________ affects mammary glands; _______ for bone growth; _____________ ____________: activate feeding reflexes such as swallowing and licking the lips and may be involved in relaying olfactory messages _______________________ pineal gland: produces __________________ ___________ __________________________________________ nuclei axons connect hypothalamus, thalamus, cerebellum and spinal cord to send sensory information to keep the cortex alert and conscious ALSO acts as a filter for sensory input to the cortex…filters out 99% of sensory input as unimportant. Has to be inhibited in order to sleep