* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Part 2 - Doral Academy Preparatory
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Positron emission tomography wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoencephalography wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
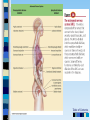
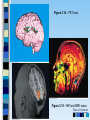
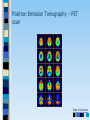
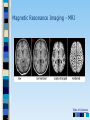
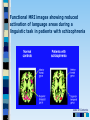
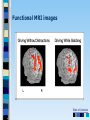
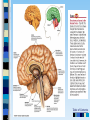
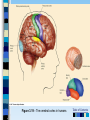
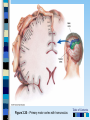
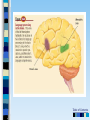
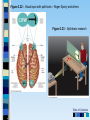
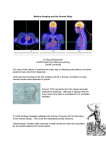
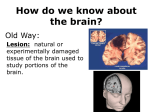
Chapter 3 Part 2 The Biological Bases of Behavior Table of Contents Table of Contents Studying the Brain: Research Methods Electroencephalography (EEG) Damage studies/lesioning Electrical stimulation (ESB) Transcortical Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Brain imaging – – computerized tomography – CT – positron emission tomography - PET – magnetic resonance imaging – MRI – functional magnetic resonance imaging – fMRI Table of Contents Figure 3-10 – Electroencephalography (EEG) Table of Contents XXX 3.13 Table of Contents Figure 3.14 – PET scan Figure 3.15 – MRI and fMRI scans Table of Contents Positron Emission Tomography – PET scan Table of Contents Magnetic Resonance Imaging - MRI Table of Contents Functional MRI images showing reduced activation of language areas during a linguistic task in patients with schizophrenia Table of Contents Functional MRI images Table of Contents Brain Regions and Functions Hindbrain – vital functions – medulla, pons, and cerebellum Midbrain – sensory functions – dopaminergic projections, reticular activating system Forebrain – emotion, complex thought – thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, cerebrum, cerebral cortex Table of Contents Table of Contents The Cerebrum: Two Hemispheres, Four Lobes Cerebral Hemispheres – two specialized halves connected by the corpus collosum – Left hemisphere – verbal processing: language, speech, reading, writing, sequential – Right hemisphere – nonverbal processing: spatial, musical, visual recognition, parallel Four Lobes: – Occipital – vision – Parietal – somatosensory – phantom limb - V. S. Ramachandran - Phantoms in the Brain – Temporal - auditory – Frontal – movement, executive control systems Primary functions and associated functions – Language – Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas – loss of language – aphasia Table of Contents Table of Contents Figure 3.19 – The cerebral cortex in humans Table of Contents Figure 3.20 – Primary motor cortex with homunculus Table of Contents Mirror Neurons An area just forward of the primary motor cortex is where “mirror neurons” were first discovered accidentally in the mid-1990s. – May play a role in the acquisition of new motor skills, • the imitation of others, • the ability to feel empathy for others, • and dysfunctions in mirror neuron circuits may underlie the social deficits seen in autistic disorders. Table of Contents The Plasticity of the Brain The brain is more “plastic” or malleable than widely assumed – Aspects of experience can sculpt features of brain structure – Damage to incoming sensory pathways or tissue can lead to neural reorganization Jill Bolte Taylor, Ph.D. – My Stroke of Insight – a neuroscientist story of her stroke and recovery Adult brain can generate new neurons – neurogenesis Table of Contents Table of Contents Figure 3.22 – Visual input with split-brain – Roger Sperry and others Figure 3.23 – Split-brain research Table of Contents