* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introductory Psychology Concepts
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Trans-species psychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
International psychology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
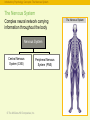
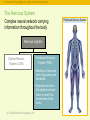
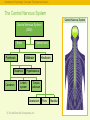
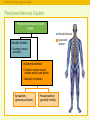
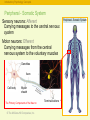
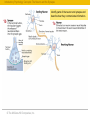
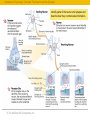
RFPGFRTJQN JS TPJGKX © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. The Brain and Behavior: • • • • Divisions of the Nervous System Neurons – Structure and Communication Structures and Functions of the Brain Brain Damage, Plasticity, and Repair © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Nervous System The Nervous System Complex neural network carrying information throughout the body Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) The Nervous System Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Nervous System The Nervous System Complex neural network carrying information throughout the body Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) • Composed of the brain and spinal cord. • Spinal cord is the primary means for transmitting messages between the brain and the rest of the body. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Central Nervous System Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Nervous System The Nervous System Complex neural network carrying information throughout the body Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Central Nervous System (CNS) • Made up of neurons with long axons and dendrites. • Branches out from the spinal cord and brain to reach the extremities of the body. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Peripheral Nervous System Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Nervous System The Central Nervous System Central Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Forebrain Midbrain Thalamus Cerebrum Spinal cord Hindbrain Hypothalamus Limbic system Corpus callosum Cerebellum © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Pons Medulla Introductory Psychology Concepts Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Somatic division Autonomic division Somatic division • Voluntary muscle activation Autonomic division • Controls smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands; • Basically involuntary Sympathetic (generally activates) © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Parasympathetic (generally inhibits) Introductory Psychology Concepts Peripheral - Somatic System Sensory neurons: Afferent Carrying messages to the central nervous system Motor neurons: Efferent Carrying messages from the central nervous system to the voluntary muscles Dendrites Axon Cell body Myelin sheath The Primary Components of the Neuron © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Terminal buttons Peripheral -Somatic System Introductory Psychology Concepts Peripheral Autonomic System Chain of sympathetic ganglia Eye: Dilates pupil Sympathetic division: Salivary glands: Inhibits flow of saliva • Fight, flight, or freeze response • Acts to prepare the body for action in stressful situations, engaging all the organism’s resources to respond to a threat. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Heart: Accelerates heartbeat Lungs: Dilates bronchi Postganglionic fibers Digestive tract: Inhibits digestion Liver: Stimulates release of glylcogen Ganglion Secretion of epinephrine by adrenal gland Urinary bladder: Inhibits bladder contraction Introductory Psychology Concepts Peripheral Autonomic System Parasympathetic division: • Maintaining normal functions • Acts to calm the body after an emergency or stressful situation has ended. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Eye: Constricts pupil Salivary glands: Stimulates flow of saliva Heart: Slows heartbeat Lungs: Constricts bronchi Digestive tract: Stimulates digestion Liver: Stimulates release of bile Urinary bladder: Contracts bladder Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Neuron and the Synapse Identify parts of the neuron and synapse and describe how they communicate information. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Neuron and the Synapse Identify parts of the neuron and synapse and describe how they communicate information. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Neuron and the Synapse Identify parts of the neuron and synapse and describe how they communicate information. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Introductory Psychology Concepts: Resting Potential and Action Potential Describe the ions used in maintaining the resting potential and in producing the action potential. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Introductory Psychology Concepts: Resting Potential and Action Potential Describe the ions used in maintaining the resting potential and in producing the action potential. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Introductory Psychology Concepts: Resting Potential and Action Potential Describe the ions used in maintaining the resting potential and in producing the action potential. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Introductory Psychology Concepts: Resting Potential and Action Potential Describe the ions used in maintaining the resting potential and in producing the action potential. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Introductory Psychology Concepts: Resting Potential and Action Potential Describe the ions used in maintaining the resting potential and in producing the action potential. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.