* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 01Integrated Normal Cells of CNS
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
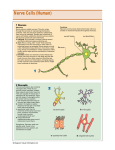
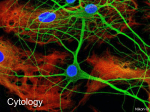
NORMAL CELLS OF CNS OBJECTIVES: At the end of this lecture, you should describe the microscopic structure and the function of: 1- Neurons: - Cell body (perikaryon). - Processes: An axon and dendrites. 2- Neuroglia: - Astrocytes. Oligodendrocytes. Microglia. Ependymal cells. Neuron Components: 1. Cell body (Perikaryon) 2. Processes : a. An axon: only one b. Dendrites: one or more TYPES OF NEURONS Based on number of processes 1. Pseudounipolar neurons. 2. Bipolar neurons. 3. Multipolar neurons. TYPES OF NEURONS Based on number of processes Axon Has one process only, that divides into two branches; one acts as a dendrite and the other as an axon. e.g. Mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve and dorsal root (spinal) ganglion. Dendrite 1. Unipolar (Pseudounipolar) neuron (rounded neuron): TYPES OF NEURONS Based on number of processes 2. Bipolar Neuron (spindle-shaped neuron): Has two processes (one arising from each pole of the cell body). One of them is the dendrite and the other is the axon, e.g. retina & olfactory epithelium. Dendrite TYPES OF NEURONS Based on number of processes 3. Multipolar neuron: Has one axon and multiple dendrites. Types of multipolar neurons: A. Stellate neuron: • The commonest type. • Distributed in most areas of CNS, e.g. anterior horn cells of the spinal cord TYPES OF NEURONS Based on number of processes B. Pyramidal neurons: • Distributed in motor area 4 of the cerebral cortex. C. Pyriform neurons: • Pear-shaped, e.g. Purkinje cells of cerebellar cortex CELL BODY (Perikaryon) Structure of cell body: 1. Nucleus: • Single, usually central, rounded and vesicular with prominent nucleolus. 2. Cytoplasm. CELL BODY (Perikaryon) Cytoplasm: Its main components include: 1. Nissl bodies: Are basophilic patches of rER and free ribosomes in the cell body and bases of wide dendrites. CELL BODY (Perikaryon) Cytoplasm: 2. Neurofilaments: Are intermediate filaments which are bundled together to form neurofibrils. Are found in the cell body, axon and dendrites. 3. Microtubles: Are found in the cell body, axon and dendrites. 4. Golgi apparatus: Surrounds the nucleus all around. 5. Mitochondria: Are numerous. CELL BODY (Perikaryon) Cytoplasm: 6. Centriole: Most adult neurons have only one rudimentary centriole, so they cannot divide. 7. Some fat and glycogen granules. 8. Pigments: - Lipofuscin pigments (in old age). - Melanin pigments (in neurons of substantia nigra of the midbrain). TYPES OF NERVE FIBERS IN CNS 1- Unmyelinated without neurilemmal sheath (in grey matter). 2- Myelinated without neurilemmal sheath (in white mater). NEUROGLIA Definition: Are group of cells that act as the supportive tissue of CNS. Types: 1- Astrocytes. 2- Oligodendrocytes. 3- Microglia. 4- Ependyma. 1. Astrocytes They are the commonest type of neuroglia cells. They are found in both the grey and white matter. They are star-shaped cells with numerous long processes. 1. Astrocytes Types: 1. Protoplasmic astrocytes: – Are found in the grey matter of CNS. – Their processes branch extensively. 2. Fibrous astrocytes: – Are found in white matter of CNS. – Their processes have fewer branches but longer. Functions of Astrocytes 1. Repair of injury of CNS tissue (gliosis). 2. Supportive and nutritive functions to the neurons. 3. Participate in the formation of bloodbrain barrier. 2. Oligodendrocytes Are branching cells with few, short processes. They are distributed in the grey and white matter of CNS. Functions: 1. Formation of myelin sheath in the CNS. 2. Insulation of nerve fibers. 3. Microglia Are spindle-shaped cells with branching processes raise from each pole of the cell. Are distributed in the grey and white matter of CNS. Are rich in lysosomes. Their main function is phagocytosis. 4. Ependymal cells Are simple columnar epithelial cells (partially ciliated) lining the brain ventricles and the central canal of spinal cord. Summary / Key words Neurons: Types of neurons: pseudounipolar bipolar multipolar: stellate, Pyramidal, Pyriform. Components: Cell body Processes: Axon and dendrites. Types of nerve fibers in CNS: Unmyelinated, Myelinated. Neuroglia: 1- Astrocytes. 2- Oligodendrocytes. 3- Microglia. 4- Ependyma. Good Luck