* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Exam 1 Which of the
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Spinal cord wikipedia , lookup
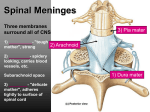
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Exam 1 Which of the following is true in regards to the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)? a. Function is fight or flight b. Craniosacral from CNS to PNS c. Thoracolumbar from CNS to PNS d. Leaves the CNS via white rami and exits the trunk via gray rami What nerves are associated with PNS? a. CN III, VI, VII, IX, sacral Nerves 2-4 b. CN VI, VII, IX, X, sacral Nerves 2-4 and pelvic splanchnics c. CN III, VII, IX, X, sacral Nerves 2-4 and pelvic splanchnics d. CN VI, IX, and X, sacral Nerves 2-4 The CNS is only the brain and spinal cord, whereas the parasympathetic system has everything else. Only the PNS has somatic and visceral components. a. True b. False Which of the following is involuntary? a. Visceral b. Somatic c. ANS d. A and C e. B and C Which of the following is voluntary? a. Visceral b. Somatic c. ANS d. A and C e. B and C Which of the following is in response to stimulation and the direction of the signal is descending from CNS to the body? a. Ventral root b. Dorsal root c. Afferent d. Efferent e. A and D f. B and C 7. Fill in the blanks of the following flow chart of the nervous system circuit: _________ stimulation: pain, pressure, movement of limbs, GI tube contraction actions generate sensory responses from affected tissue/organ To spinal cord via sensory Nerves: all enter spinal cord via _________ __________ in spinal cord To the brain via spinal cord; brain interprets stimuli and generates a response Muscle Motor: initiaes contraction _______ stimulation: brain sending signals to initiate various response 8. Cervical nerves are numbered for the vertebra _____ the nerve except for cervical nerve ____. a. Above, 7 b. Above, 8 c. Below, 7 d. Below, 8 9. The ANS is a ____ neuron system a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. all of the above 10. The parasympathetic system is: a. Visceral b. Vegetative functions c. Sensory d. All of the above e. None of the above 11. Primary neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system are in the _____ and are _____ preganglionic fibers. a. Cerebellum, long b. Cerebrum, short c. Brain stem, long d. Spinal cord, short 12. Secondary neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system are _____ and are in the wall of the organ innervated. a. Long b. Short 13. Fill in the following system for the sympathetic system: primary neurons leave the CNS via the _______ the sympathetic trunk is made up of _______ ________, one of each vertrebal level and the preganglionc fibers run between these they then go to _________ travel to ______ of sympathetic trunks which parallels the spinal column and leave as _______ only in the ______________ region 14. Preganglionc fibers in the sympathetic trunk have 3 options. Fill in each of the following cycles for each of the options: synapse in ganglion they enter leave via _______ ramus return to _______ rami distribute via ventral and dorsal rami to entire body a. b. travel up or down the trunk to reach the appropriate level they want to innervate synapse and leave via _____ ramus at that level return to ______ ramus and distribute throughout entire field of nerves at that level c. pass through the ______ chain w/out synapsing exit chain as _____ nerves travel to sympathetic ganglia on and near _____ in abdomen and pelvic revions ___-ganglionics will then travel with teh arteries 15. There is an exception to the above options in the neck where 3 major ganglia formed from fusion of cervical ganglia. The most important one is the superior cervical ganglion (SCG) and is the terminal ganglion of the _______ chain in the ______ regions and is all of the sympathetic innervation to the face and deeper structures of the head from SCG. a. Parasympathetic, upper b. Parasympathetic, lower c. Sympathetic, upper d. Sympathetic, lower 16. What gives rise to the nervous system in development? a. Endoderm b. Mesoderm c. Ectoderm d. All of the above 17. The neural folds form the neural tube which differentiates into the ______ a. PNS b. ANS c. CNS d. A and B e. All of the above 18. The lumen of the neural tube forms the neural canal which forms the _______ a. Ventricular system of the brain b. Central canal of the spinal cord c. Cerebellum d. A and B e. All of the above 19. The neural crest dorsolateral groups give rise to the cells that form most of the ________ a. PNS b. ANS c. CNS d. A and B e. All of the above 20. The lateral walls of the neural tube are initially composed of pseudostratified, columnar neuroepithelium. The neuroepithelial cells of the ventricular zone (ependymal layer) give rise to all neurons and macroglial cells in the spinal cord. The macroglial cells give rise to glioblasts. Which of the following gives rise the cells that play a part in the blood brain barrier? a. Oligodendrocyte b. Astrocyte c. Microglial cells d. A and B e. All of the above 21. Dorsal midline portions of the neural tube give rise to the ______ plate and the ventral portions gives rise to the _____ plate. They serve as pathways for nerve fibers crossing from one side to the other. a. Roof, floor b. Floor, roof c. Roof, roof d. Floor, floor 22. A shallow longitudinal groove that is produced from lateral wall thickenings. It functions to separate the:_____ and disappears in adult spinal cord but is retained in rhomboid fossa of the brain stem (aka 4th ventricle floor) a. Alar and basal plates b. Afferent and efferent c. Sensory and motor functions d. B and C e. All of the above 23. These plates have cell bodies that contribute to the formation of the ventral and lateral gray horns: a. Anterior b. Posterior c. Basal d. Alar e. A and C f. B and D 24. What is more substantial? a. Dorsal median fissure b. Dorsal median septum c. Ventral median fissure d. Ventral median septum 25. Neural crest cells give rise to _____ neurons in the _____ root ganglia and function much like the first neuron in development. a. Unipolar, dorsal b. Unipolar, ventral c. Bipolar, dorsal d. Bipolar, ventral 26. The vertebral column and dura mater grow faster than the spinal cord and so the spinal cord will eventually be shorter. Distal to the caudal end of the spinal cord is ______ that forms a long fibrous thread called the terminal filum (filum terminale) and extends from the medullary cone and attaches to the periosteum of the fist coccygeal vertebra. a. Dura mater b. Pia mater c. Arachnoid d. Subarachnoid 27. Fill in the following chart. It is an important chart for this upcoming exam. 3 primary vesicles 5 secondary Adult derivatives Adult derivatives vesicles of walls of cavities Forebrain (__________________) _____________________ (Mesencephalon) Hindbrain (____________________) Telencephalon ________________ Lateral ventricle ___________________ Mesencephalon Thalami ___________________ ___________________ _________________ ____________________ Pons and Cerebellum __________________ Myelencephalon ______________ Lower 4th ventricle 28. The cervical flexure forms between the hindbrain and the spinal cord. a. True b. False 29. This cranial nerve (motor fiber) innervates ocular, tongue, external neck: a. General somatic efferent (GSE) b. Special visceral efferent (SVE) c. General visceral efferent (GVE) 30. Which of the following accurately describes the above fibers? a. Derived from embryonic pharyngeal arches b. Axons innervate involuntary (smooth) muscles or glands c. Axons innervate muscles derived from sources OTHER than embryonic pharyngeal arches 31. This cranial nerve (motor fiber) innervates face, palate, pharynx, and larynx (CN V and VII) a. General somatic efferent (GSE) b. Special visceral efferent (SVE) c. General visceral efferent (GVE) 32. Which of the following accurately describes the above fibers? a. Derived from embryonic pharyngeal arches b. Axons innervate involuntary (smooth) muscles or glands c. Axons innervate muscles derived from sources OTHER than embryonic pharyngeal arches 33. Which of the following has axons that innervate involuntary (smooth) muscles or glands a. General somatic efferent (GSE) b. Special visceral efferent (SVE) c. General visceral efferent (GVE) 34. Which of the following cranial nerves (sensory fibers) is responsible for vision, hearing, and balance? a. General visceral afferent (GVA) b. General somatic afferent (GSA) c. Special visceral afferent (SVA) d. Special somatic afferent (SSA) 35. Which of the following cranial nerves (sensory fibers) is responsible for touch, pressure, heat, and cold that transmits general sensation from skin and mucous membranes? a. General visceral afferent (GVA) b. General somatic afferent (GSA) c. Special visceral afferent (SVA) d. Special somatic afferent (SSA) 36. Which of the following cranial nerves (sensory fibers) is responsible for taste and smell? a. General visceral afferent (GVA) b. General somatic afferent (GSA) c. Special visceral afferent (SVA) d. Special somatic afferent (SSA) 37. Which of the following cranial nerves (sensory fibers) is responsible for carrying sensation from the kidneys? a. General visceral afferent (GVA) b. General somatic afferent (GSA) c. Special visceral afferent (SVA) d. Special somatic afferent (SSA) 38. In the caudal myelencephalon (closed portion that resembles the spinal cord – aka medulla) the neuroblasts from alar plates migrate and form isolated gray matter and are sensory in nature (b/c dorsal). _______ is medial and ______ is lateral a. Gracile nuclei, cuneate nuclei b. Cuneate nuclei, gracile nuclei 39. The ventral area of the medulla has pyramids with _______ fibers that descend from developing cerebral cortex and will eventually form a tract. a. Spinothalmic b. Corticospinal c. Spinocerebral d. Dorsal columns 40. The rostral myelencephalon is the open part of the medulla and the cavity here will form the _____ ventricle. As the walls of move laterally the alar plates will lie lateral to the basal plates, thus the motor nuclei will form _____ to the sensory nuceli. a. 3rd, medially b. 3rd, laterally c. 4th, medially d. 4th, laterally 41. The neuroblasts of the alar and basal plates of the medulla form ____ and _____ columns respectively on each side. a. 3,4 b. 4,3 c. 3,3 d. 4,4 42. The ____ is good identification marker for the medulla and aids is motor control: a. Choroid plexus b. Olivary nucleus c. Ventricle d. All of the above 43. What does the basal plate neuroblast in the metencephalon that innervates submandibular and sublingual glands: a. GSE b. SVE c. GVE 44. What does the basal plate neuroblast in the metencephalon that innervates abducens nerve nucleus: a. GSE b. SVE c. GVE 45. What does the basal plate neuroblast in the metencephalon that innervates 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arch musculature: a. GSE b. SVE c. GVE 46. What does the alar plate neuroblast in the metencephalon that has CN VII (taste)? a. GVA b. SVA c. GSA d. SSA 47. What does the alar plate neuroblast in the metencephalon that has CN VIII? a. GVA b. SVA c. GSA d. SSA 48. What does the alar plate neuroblast in the metencephalon that has CN VII? a. GVA b. SVA c. GSA d. SSA 49. What does the alar plate neuroblast in the metencephalon that has trigeminal nerve? a. GVA b. SVA c. GSA d. SSA 50. The cerebellum forms from the metencephalon from thickenings of the dorsal parts of the _____ plates (cerebellar swellings) and project into the ____ ventricle: a. Alar, 3rd b. Alar, 4th c. Basal, 3rd d. Basal, 4th 51. Neuroblasts from alar plates of the midbrain (sensory) migrate into the tectum (roof) and aggregate to form 4 large groups of neurons. Which paired colliculi are responsible for auditory reflexes? a. Superior colliculi b. Inferior colliculi c. Anterior colliculi d. Posterior colliculi 52. Neuroblasts from alar plates of the midbrain (sensory) migrate into the tectum (roof) and aggregate to form 4 large groups of neurons. Which paired colliculi are responsible for visual reflexes? a. Superior colliculi b. Inferior colliculi c. Anterior colliculi d. Posterior colliculi 53. Neuroblasts from basal plates of the midbrain (motor) have groups of neurons in tegmentum (covering) of the midbrain. The group of neurons that aid in control over the limb flexors is: a. Nuclei of 3rd and 4th cranial nerves b. Rubrospinal tract c. Reticular nuclei d. Substantia nigra 54. Neuroblasts from basal plates of the midbrain (motor) have groups of neurons in tegmentum (covering) of the midbrain. The group of neurons that are involved in virtually every activity: a. Nuclei of 3rd and 4th cranial nerves b. Rubrospinal tract c. Reticular nuclei d. Substantia nigra 55. Neuroblasts from basal plates of the midbrain (motor) have groups of neurons in tegmentum (covering) of the midbrain. The group of neurons that aids in regulation of motor functions: a. Nuclei of 3rd and 4th cranial nerves b. Rubrospinal tract c. Reticular nuclei d. Substantia nigra 56. The ____ ventricles communicate with the 3rd ventricle (diencephalon) via the interventricular foramina (of Monroe). a. Medial b. Lateral c. Anterior d. Posterior














![ANAT20006: Principles of Human Structure [Notes] Terminology (L1](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000528493_1-289a738cc7e5c0b70271c1a1332b2a90-150x150.png)