* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download General PLTW Document - Buncombe County Schools
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
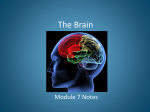
Activity 8.2.4 Brain Anatomy Introduction The brain is a complex organ composed of lobes, ventricles, and systems that are organized into specialized regions. These regions are responsible for functions such as speech, emotion, and memory as well as vision, hearing, and taste. Other regions of the brain control involuntary functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature. The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord and is the processing center for the nervous system. In the previous activities you investigated the five senses: sight, touch, taste, smell and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and cold throughout the body. A specialized structure within the brain is the thalamus. With the exception of smell, the thalamus acts as a relay station for all the senses. The thalamus sorts the important information from the insignificant before sending information to the cerebral cortex of the brain. In this activity you will explore a computer animation to learn about the structure and functions of the human brain. Equipment Laboratory Journal Pencil Colored pencils or crayons Computer with Internet access © 2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc. PLTW Gateway – Medical Detectives Activity 8.2.4 Brain Anatomy – Page 1 Procedure 1. Access and explore the PBS website, 3-D Brain Anatomy, at http://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain/3d/index.html 2. Label and color the following structures on the exterior of the brain Cerebrum, made of 4 lobes: o Frontal lobe (purple) o Parietal lobe (red) o Occipital lobe (orange) o Temporal lobe (brown) Cerebellum (green) Brain Stem (yellow) © 2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc. PLTW Gateway – Medical Detectives Activity 8.2.4 Brain Anatomy – Page 2 3. Label and color the following structures on the interior of the brain Cerebrum, made of 4 lobes: o Frontal lobe (purple) o Parietal lobe (red) o Occipital lobe (orange) o Temporal lobe (brown) Cerebellum (green) Brain Stem (yellow) Corpus Callosum (blue) Limbic System (label) o Pineal Gland o Hypothalamus o Amygdala o Hippocampus Thalamus (pink) Free images courtesy of Wikimedia Commons http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Main_Page © 2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc. PLTW Gateway – Medical Detectives Activity 8.2.4 Brain Anatomy – Page 3 4. In previous activities you investigated the five senses. Use the PBS website to locate the part(s) of the brain responsible for: Vision optical nerves, thalamus, and occipital lobes Hearing auditory nerves, temporal lobes Smell olfactory nerves, olfactory bulbs, olfactory center, hypothalamus Touch nerves, thalamus, parietal lobe Taste frontal lobe, hypothalamus, amygdala _____ 5. What structure acts as a relay station for all senses except smell? thalamus 6. Identify the part(s) of the brain involved with: Short-term memory parietal, upper temporal, and occipital lobes Long-term memory hippocampus, frontal lobes, thalamus, and hypothalamus Movement cerebellum 7. What part of the brain controls essential survival functions such as breathing and heart beat? Brain stem Conclusion 1. What region of the brain is responsible for complex thinking such as memory, speech, emotion, planning, and reasoning? Explain. Frontal lobe; largest of the cerebrum’s 4 lobes, well connected with the limbic system 2. Why is the brain stem sometimes called the “reptilian brain”? This is the oldest and most basic brain region 3. Why do you “see stars” when you hit the back of your head? You may damage the occipital lobe which is connected to the optical nerves © 2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc. PLTW Gateway – Medical Detectives Activity 8.2.4 Brain Anatomy – Page 4 © 2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc. PLTW Gateway – Medical Detectives Activity 8.2.4 Brain Anatomy – Page 5