* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nonassociative Learning
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Emotion perception wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Perceptual learning wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Mental chronometry wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
C1 and P1 (neuroscience) wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Negative priming wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Conditioned place preference wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Lateralized readiness potential wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Response priming wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
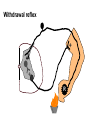
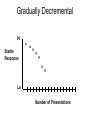
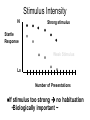
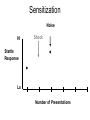
Nonassociative Learning Lecture 3 Reflexes Inherited behaviors via genes Smallest unit of organized behavior sensory receptors neurons effectors Learning modification of existing behavior initially reflexive behavior ~ Withdrawal reflex + + + R 2 categories of learning Similar characteristics Nonassociative modification of reflexes (unconditional responses) Habituation Sensitization Associative Respondent learning Operant learning ~ Nonassociative Learning: Habituation Living near the train tracks Habituation response to repeated stimulus stimulus specific Ignore biologically unimportant stimuli Universal in animal kingdom evolved early protozoans ~ Adaptiveness of Habituation Conserves resources energy attention Stimuli w/o consequences response diminishes ~ Stickleback Fish Males defend territory Attack when others approach If other males do not enter territory Attack response diminishes ~ Habituation Phenomena Gradually Decremental Hi Startle Response Lo Number of Presentations Spontaneous Recovery Learning is relatively permanent Reinstatement of reflexive response due only to passage of time stimulus may again have consequences ~ Spontaneous Recovery Hi Startle Response Stimulus Time Passes Lo Number of Presentations Is it fatigue? Temporary physiological change Motor? Sensory? Dishabituation introduce extraneous stimulus recovery of habituated response ~ Dishabituation: Example Tone (Noise) startle response in rat Repeat tone habituation Flash a light Present tone startle response ~ Dishabituation Hi Habituation occurs *Light (New) + Noise Startle Response Lo Number of Presentations Dishabituation Decrease in response not due to fatigue animal capable of response signals a new situation Response is inhibited by activity of neurons ~ Generalization Organism reacts to similar stimuli in the same way Greater the difference... less habituation evident Color perception in infants ~ Effect of Stimulus Intensity Stimulus intensity Intense stronger response Weak weaker response Which stimulus will the organism habituate to more quickly? ~ Stimulus Intensity Hi Strong stimulus Startle Response Weak Stimulus Lo Number of Presentations stimulus too strong no habituation •Biologically important ~ If Sensitization Increased responsiveness Following a noxious stimulus Less stimulus specific than habituation general increase in vigilance sensitized responses to wide range of stimuli Adaptiveness ~ Sensitization Noise Hi Shock Startle Response Lo Number of Presentations Duration:Habituation & Sensitization Can be short term lasts hours Change in neural activity or long term several weeks change in neural structure ~ Habituation & Eating 1st taste most pleasant # tastes pleasantness Role in meal termination e.g., popcorn, cashews Not just for taste also texture, shape, odor, etc. ~ Habituation & Eating: Rats Cabanac (1971) Steady flow of sucrose into mouth tasty disinterest aversion Allow rats to eat all rat chow they want voluntarily stop offer sucrose: eat just as many calories ~ Habituation & Eating: Humans Rolls (1990) Preference ratings for foods given meal of one of foods rated again rating for just-eaten food Given 2 meals different foods same amount eaten same food 2nd meal ate less ~