* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.7 Learning and Memory
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
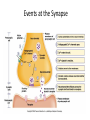
8.6 Learning and Memory Topic 8 Specification • 14 Describe how animals, including humans, can learn by habituation. • 16 Discuss the moral and ethical issues relating to the use of animals in medical research from two ethical standpoints. Where are memories stored? – Read page 244 – Q 8.51• parietal lobe , temporal lobe, hippocampus – Q 8.52• involved in forming new long-term memory but NOT involved in recalling long-term memory How are memories stored? – Read page 244-247 – How are memories created? • Pattern of connections - which other neurons is each neuron is connected to. • Strength of the synapse Events at the Synapse Habituation – get used to it! • Wearing socks • Birdsong • Noisy computer • the diminishing of an innate response to a frequently repeated stimulus • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dlilZh60qdA Habituation A type of learning, if you are exposed repeatedly to the same stimulus after a while you are neither aware of it nor respond to it. What is the advantage of habituation? • Animals can ignore unimportant stimuli so that limited sensory, attention and memory resources can be concentrated on more threatening or rewarding stimuli. Habituation in Sea Slugs – Why was the sea slug used to study the change in synapse strength? • No fundamental difference between nerve cells and synapses in humans and slugs • Only 20,000 neurons in the sea slug so simpler to study than the human. • Large accessible neurones – Q 8.53 Habituation in sea slugs – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yLa-cXg8BwM – Identify the stages in the reflex arc when water is sprayed at the syphon and then the gill is withdrawn Habituation – Describe in your own words how habituation is achieved. • Ca2+ ion channels become less responsive so they don’t open and less or no Ca ions diffuse into the neuron. • Less neurotransmitter is released • Less depolarisation in the post-synaptic neurone • May not reach the threshold so no action potential is triggered in the motor neurone – Activity 8.17 Activity 8.17 Compare habituation and sensitisation in terms of• The effect on sensitivity to stimuli. • What happens at the synapse. Compare habituation and sensitisation in terms of• After repeated stimuli habituation decreases the awareness and response to that stimulus. Sensitisation will result in an increase in awareness to all stimuli. • Two neurons are involved in habituation- the Ca2+ channels in the pre-synaptic neuron become less responsive- less Ca uptake. • In sensitisation three neurones are involvedSerotonin released by neurones from the receptor of the first stimulus increase the uptake of Ca in the pre-synaptic neuron of other sensory neurons. Habituation vs Long term memory – Memories are created either by changing the pattern of connection or by changing the strength of the synapses. Which is habituation an example of? • Changing the strength of the synapse – How are long term memories created? • Increase in the number of synaptic connections Activity 8.16 Can snails become habituated to a stimulus? • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MslbUpxC1-A • Use this movie to collect and present data as stated in steps 1-6 • Questions 1-6 • Going Further: Introduce Statistical test and null hypothesis- Statistics and the Unit 6 exam slide show, with Unit 3 and 6 booklet The ethics of animal research • Who would not accept any experimentation on animals? • Do you believe some experimentation on animals is acceptable? Why? Any research? Any animal? • What is a utilitarian approach to the use of animals? • https://www.beep.ac.uk/content/425.0.html Ethics of using animals in medical research Reasons for using animals in medical research Reasons against using animals in medical research Animals which are tested on are provided with good food, water, veterinary treatment (better than in the wild) and the ability to express normal behaviour The welfare of animals is threatenedthey may experience pain, or may not be able to express normal behaviour Although animals are used and may die in animal testing this is by far outweighed by the good that comes form the testing- cures, treatment of disease reducing the suffering of many people- utilitarian argument They have a right to freedomnot being incarcerated for animal testing Animals are not able to give consent- they have a right to do this