* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Psychologists Study the Brain
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Positron emission tomography wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
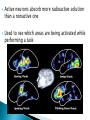
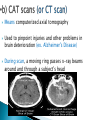
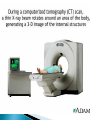
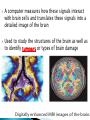
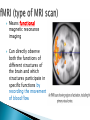
Also called psychobiologists Psychologists who map the brain’s fissures (grooves on the brain which appear as a deep fold) and inner recesses Methods include: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ 1) 2) 3) 4) Recording Stimulating Lesioning Imaging Electrodes inserted into the brain to record electrical activity ◦ Recall the brain generates enough electricity to power a low-wattage light bulb! Possible to detect minute (small) electrical changes that occur when neurons (brain cells) fire EEG (electroencephalograph) records electrical activity of whole areas of the brain Have found that overall electrical activity of the brain rises and falls rhythmically and that the pattern of the rhythm depend on whether a person is awake, drowsy, or sleepy Rhythms(brains waves), occur because the neurons in the brain tend to increase or decrease their amount of activity in unison (together) Electroencephalogram (EEG) –a device that records the electrical activity of the brain. Scans • Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT or CT) detect brain damage & measure activity as subjects perform a task. Fast Fact - Acupuncture is based on the belief that by inserting needles into various parts of the body, they can interrupt pain messages sent to the brain, thus alleviating the pain or treating the illness Electrical Stimulation -Electric stimulation of one part of the brain causes specific sensations in the body. Electrodes used to set off (cause) the firing of neurons (brain cells) Brain surgeon Wilder Penfield stimulated the brains of his patients during surgery to determine what functions the various parts of the brain perform so as to localize (focus on) the malfunctioning part for which surgery was required https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=68MiW2KK1us Stimulation techniques have been used with terminal cancer patients to relieve intolerable pain without using drugs and in experiments done to control violent emotional behaviours in uncontrollable patients Scientists sometimes create lesions by cutting or destroying parts of an animal’s brain. If the animal behaves differently after the operation, they assume that the destroyed brain area is involved with that type of behaviour Psychologists can learn from tragedies when some people suffer accidents which involve the brain. They can see the results of physical brain damage & its affects on people. Psychobiologists try to draw a connection between the damaged parts of the brain and a person’s behaviours, such as Phineas Gage in 1848 P H I N E A S G A G E Students write down the following questions in your notes. Write your answers in complete sentences. What type of scanning device is used to analyze Gage’s brain? What part of Gage’s Brain was damaged? How did Phineas Gage change after the accident? Psychobiologists use PET scans, CAT scans and MRI scans Means Positron emission tomography Captures a picture of the brain as different parts are being used Involves injecting a slightly radioactive solution into the blood and then measuring the amount of radiation absorbed by brain cells Active neurons absorb more radioactive solution than a nonactive one Used to see which areas are being activated while performing a task About 1 hour after the injection, the PET scan is done. The PET scanner looks like a large, doughnut-shaped scanner, similar to a CT scanner. The person sits or lies down on the exam table and is asked to stay very still. Sometimes PET scan can be done along with CT or MRI. After the scan, the radioactive material quickly loses its radioactivity. It passes out of the body through the urine or stool (feces) Means computerized axial tomography Used to pinpoint injuries and other problems in brain deterioration (ex. Alzheimer's Disease) During scan, a moving ring passes x-ray beams around and through a subject’s head Radiation is absorbed in different amounts depending on the density (“weight”) of the brain tissue Computers measure the amount of radiation absorbed and transform this information into a three-dimensional view of the brain A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging test that uses a computer to put a series of special x-ray images together to create detailed 3-dimensional images of organs, tissues, bones and blood vessels in the body. Some CT scans require a contrast medium to show organs and abnormalities more clearly. A CT scan is also called computerized axial tomography (CAT) scan. A CT scan can be done on almost any body part. It can show detailed views of many different types of tissue, such as the: brain, airways, lungs, bones, soft tissue and blood vessels Means magnetic resonance imaging Enables researchers to study both activity and brain structures Combines features of both PET and CAT scans Involves passing nonharmful radio frequencies through the brain A computer measures how these signals interact with brain cells and translates these signals into a detailed image of the brain Used to study the structures of the brain as well as to identify tumours or types of brain damage A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnetic forces and radio-frequency (RF) waves to make detailed 3-dimensional pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and most other internal body structures. Some MRI scans require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal devices inside their body (such as a pacemaker, implanted port or pump). The magnetic force is so strong that it can damage or dislodge these devices. In most cases, MRI can be done on people who have joint replacements, surgical clips or screws. Means functional magnetic resonance imaging Can directly observe both the functions of different structures of the brain and which structures participate in specific functions by recording the movement of blood flow How Does an MRI Work? (1:21) http://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=1CGzknV06g&list=PL1872FCF16467E 980 How Does a PET Scan Work? (1:33) http://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=GHLBcCv4rqk&feature=c4overviewvl&list=PL1872FCF16467E980 How CT Scan Machine Works (1:01) http://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=tqGmqRrxajQ