* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Okazaki Fragments
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
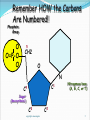
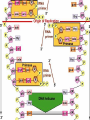
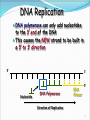
1 Replication Facts DNA has to be copied before a cell divides DNA is copied during the S or synthesis phase of interphase New cells will need identical DNA strands 2 Replication requires the following steps 1-Unwinding Begins at Origins of Replication Two strands open forming Replication Forks (Y-shaped region) New strands grow at the forks 5’ Parental DNA Molecule 3’ Replication Fork 3’ copyright cmassengale 35’ 2-Complementary base pairing Before new DNA strands can form, there must be RNA primers present to start the addition of new nucleotides Primase is the enzyme that synthesizes the RNA Primer DNA polymerase can then add the new nucleotides copyright cmassengale 4 Remember HOW the Carbons Are Numbered! Phosphate Group O O=P-O O 5 CH2 O N C1 C4 Nitrogenous base (A, G, C, or T) Sugar (deoxyribose) C3 copyright cmassengale C2 5 copyright cmassengale 6 DNA Replication DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3’ end of the DNA This causes the NEW strand to be built in a 5’ to 3’ direction 5’ 3’ Nucleotide DNA Polymerase RNA Primer 5’ Direction of Replication 7 Synthesis of the New DNA Strands The Leading Strand is synthesized as a single strand from the point of origin toward the opening replication fork 5’ 3’ 5’ Nucleotides DNA Polymerase copyright cmassengale RNA Primer 8 Synthesis of the New DNA Strands The Lagging Strand is synthesized discontinuously against overall direction of replication This strand is made in MANY short segments It is replicated from the replication fork toward the origin Leading Strand 5’ 3’ 5’ 3’ DNA Polymerase RNA Primer 3’ 5’ 3’ 5’ Lagging Strand copyright cmassengale 9 Lagging Strand Segments Okazaki Fragments - series of short segments on the lagging strand Must be joined together by an enzyme DNA Polymerase Okazaki Fragment RNA Primer 5’ 3’ Lagging Strand 3’ 5’ 10 Joining of Okazaki Fragments The enzyme Ligase joins the Okazaki fragments together to make one strand DNA ligase 5’ 3’ Okazaki Fragment 1 Lagging Strand Okazaki Fragment 2 3’ 5’ 11 3-Jioning The complementary nucleotides join to form new strands by DNA polymerase. Each daughter DNA molecules contains an old new strand. Replication of Strands Replication Fork Point of Origin 13 END