* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch24- Memory Systems
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Procedural memory wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Collective memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
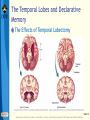
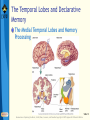
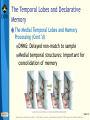
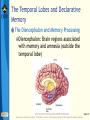
Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e Chapter 24: Memory Systems Slide 1 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Introduction Learning and remembering distinguishes naïve from mature brain Relationship between visual development and learning Similar mechanisms in different cortical areas Memories range from stated facts to ingrained motor patterns Anatomy: Several memory systems Evident from brain lesions Slide 2 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Types of Memory and Amnesia Learning Acquisition of new information Memory Retention of learned information The way information is stored may change over time Declarative memory (explicit) Facts and events Nondeclarative memory (implicit) Procedural memory- skills, habits, behaviors Slide 3 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Types of Memory and Amnesia Long-Term, Short-Term, and Working Memory Sensory information Short-term memory Consolidation Long-term memory Short-term memory Sensory information Consolidation Long-term memory Time Working memory: Temporary information storage Slide 4 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Types of Memory and Amnesia Amnesia Amnesia: Serious loss of memory and/or ability to learn Causes: Concussion, chronic alcoholism, encephalitis, brain tumor, or stroke Common amnesia: Limited amnesia Dissociated amnesia: Amnesia, no other cognitive deficit (rare) Slide 5 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Types of Memory and Amnesia Amnesia (Cont’d) Memory loss related to time Retrograde amnesia Forget things you already knew Anterograde amnesia Inability to form new memories Transient global amnesia: Shorter period Symptoms: Disoriented, ask same questions repeatedly; Attacks subside in couple of hours; Permanent memory gap Slide 6 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Search for the Engram Lashley’s Studies of Maze Learning in Rats Engram: memory trace Slide 7 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Search for the Engram Hebb and the Cell Assembly External events are represented by cortical cells Cells reciprocally interconnected reverberation Active neurons—cell assembly Consolidation by “growth process” “Fire together, wire together” Hebb and the engram Widely distributed among linked cells in the assembly Could involve neurons involved in sensation and perception Slide 8 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Search for the Engram Hebb’s Cell Assembly and Memory Storage Slide 9 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Search for the Engram Localization of Declarative Memories in the Neocortex Experiments—macaque monkeys Differentiate objects based on shapes Lesion made in area IT Cannot discriminate Does not remember stimulus Studies in humans Slide 10 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Search for the Engram Electrical Stimulation of the Human Temporal Lobes Penfield’s experiments Electrical stimulation of the temporal lobe Complex sensations Penfield’s patients: Sensations like hallucinations, recall past experiences Temporal lobe: Role in memory storage Temporal lobe stimulation Different from stimulation of other areas of neocortex Slide 11 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Temporal Lobes and Declarative Memory The Effects of Temporal Lobectomy Slide 12 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Temporal Lobes and Declarative Memory The Medial Temporal Lobes and Memory Processing Slide 13 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Temporal Lobes and Declarative Memory The Medial Temporal Lobes and Memory Processing (Cont’d) DNMS: Delayed non-match to sample Medial temporal structures: Important for consolidation of memory Slide 14 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Temporal Lobes and Declarative Memory The Diencephalon and Memory Processing Diencephalon: Brain regions associated with memory and amnesia (outside the temporal lobe) Slide 15 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Temporal Lobes and Declarative Memory The Diencephalon and Memory Processing Korsakoff’s Syndrome Symptoms: Confusion, confabulations, severe memory impairment, and apathy Alcoholics: Develop thiamin deficiency Leads to symptoms: Abnormal eye movements, loss of coordination, tremors Treatment: Supplemental thiamin Thiamin deficiency: Structural brain damage Slide 16 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Temporal Lobes and Declarative Memory Memory Functions of the Hippocampus Role of the medial temporal lobes Declarative memory processing or consolidation Slide 17 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Temporal Lobes and Declarative Memory Memory Functions of the Hippocampus Spatial Memory and Place Cells Morris water maze Slide 18 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Temporal Lobes and Declarative Memory Memory Functions of the Hippocampus Spatial Memory, Working Memory, and Relational Memory Relational memory Highly processed sensory information To hippocampus and nearby cortex Slide 19 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Striatum and Procedural Memory Two elements of basal ganglia Striatum Caudate nucleus Putamen Rodent Recordings and Lesions in the Striatum Lesions to striatum: Disrupts procedural memory Damaged hippocampal system: Degraded performance on standard maze task Lesion in striatum: Impaired performance of the light task; Double dissociation Slide 20 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Striatum and Procedural Memory Habit Learning in Humans and Nonhuman Primates Striatum in humans plays a role in procedural memory Slide 21 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Neocortex and Working Memory The Prefrontal Cortex and Working Memory Primates have a large frontal lobe Function of prefrontal cortex: selfawareness, capacity for planning and problem solving Slide 22 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Neocortex and Working Memory The Prefrontal Cortex and Working Memory (Cont’d) Imaging Working Memory in the Human Brain Numerous areas in prefrontal cortex are involved in working memory Slide 23 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Neocortex and Working Memory Lateral Intraparietal Cortex (Area LIP) and Working Memory Area LIP: Guiding eye movements Delayed-saccade task Slide 24 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Concluding Remarks Learning and memory Occur throughout the brain Memories Duration, kind of information stored, and brain structures involved Distinct types of memory Different types of amnesia Multiple brain systems for memory storage Engrams in temporal lobe neocortex Physiological basis? Long-term memories: structural basis? Slide 25 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins End of Presentation Slide 26 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins