* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 22: Mental Illness
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
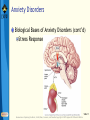
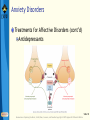
Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e Chapter 22: Mental Illness Slide 1 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Introduction Neurology Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of nervous system disorders Neurological disorders Help illustrate the role of physiological processes in normal brain function Slide 2 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Introduction Psychiatry Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of disorders that affect the mind or psyche Psychiatric disorders Examples: Anxiety disorders, affective disorders, schizophrenia Slide 3 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Mental Illness and the Brain Human behavior Product of brain activity Brain Product of two mutually interacting factors DNA Determines individualism Slide 4 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Mental Illness and the Brain Mental illness Diagnosable disorder of thought, mood, or behavior that causes distress or impaired functioning Earlier belief Disorders of the body Disorders of the mind Slide 5 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Mental Illness and the Brain Psychosocial Approaches to Mental Illness Freud’s theory: Mental illness- Unconscious and conscious elements of psyche come into conflict Skinner: Many behaviors are learned responses to the environment Maladaptive behavior Slide 6 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Mental Illness and the Brain Biological Approaches to Mental Illness General paresis of the insane Symptoms: Mania, cognitive deterioation Cause: T. pallidum infection Paul Ehrlich (1910) Penicillin (1928) Mental illnesses traced directly to biological causes Roots of mental disorders Slide 7 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Fear An adaptive response to threatening situations Innate and species-specific Learned Anxiety disorders Caused by inappropriate expression of fear Slide 8 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Common Anxiety Disorders Panic disorder Agoraphobia Obsessive-compulsive disorder Generalized anxiety disorder Specific phobias Social phobia Post-traumatic stress disorder Slide 9 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Biological Bases of Anxiety Disorders Fear evoked by threatening stimulus: Stressor Manifested by stress response Stimulus-response relationship strengthened (and weakened) by experience Stress: Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) cortisol Slide 10 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Biological Bases of Anxiety Disorders (cont’d) Stress Response Slide 11 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Regulation of the HPA Axis by the Amygdala and Hippocampus Both regulate CRH neurons Amygdala projects to bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, which activates the HPA axis Hippocampus deactivates the HPA axis Glucocorticoid receptors Feedback loop Push-pull style regulation Slide 12 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Treatments for Anxiety Disorders Psychotherapy Anxiolytic Medications Role of GABA Benzodiazepines Serotonin-selective reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) Drug target: CRH receptors Slide 13 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders A Description of Affective Disorders “Mood” Disorders Major Depression Depression Dysthymia Bipolar Disorder Manic-depressive disorder Mania Hypomania Slide 14 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Biological Bases of Affective Disorders The Monoamine Hypothesis Problems with diffuse modulatory systems Reserpine Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Imipramine Monoamine hypothesis of mood disorders Slide 15 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Biological Bases of Affective Disorders (cont’d) The Diathesis-Stress Hypothesis Genetic and nongenetic Diathesis HPA system Impact of CRH HPA function Glucocorticoid receptor Tactile stimulation process Factors of mood and anxiety disorders Slide 16 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Treatments for Affective Disorders Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): Localized electrical stimulation Advantage of ECT: Quick relief Adverse effect of ECT: Prior memories, storage of new information Structures involved: Temporal lobe Psychotherapy: Help patients overcome negative views Slide 17 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Treatments for Affective Disorders (cont’d) Antidepressants Slide 18 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anxiety Disorders Treatments for Affective Disorders Lithium Slide 19 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Schizophrenia A Description of Schizophrenia Severe mental disorder Symptoms of schizophrenia: Loss of contact with reality Three types of schizophrenia Paranoid schizophrenia Disorganized schizophrenia Catatonic schizophrenia Slide 20 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Schizophrenia Biological Bases of Schizophrenia Genes and the Environment Schizophrenia: A genetic disorder Schizophrenia and the ventricle to-brainsize ratio Other structural observation of the brains of schizophrenics The Dopamine Hypothesis: Psychotic episodes in schizophrenia triggered by activation of dopamine receptors Neuroleptic drugs Slide 21 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Schizophrenia Biological Bases of Schizophrenia (cont’d) The Glutamate Hypothesis Behavioral effects of phencyclidine (PCP) Introduced in1950s as an anesthetic Inhibits NMDA receptors Glutamate: Fast excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain, two important receptor subtypes, AMPA and NMDA Slide 22 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Schizophrenia Treatments for Schizophrenia Consists of drug therapy combined with psychosocial support Conventional neuroleptics, such as chlorpromazine and haloperidol, act at D2 receptors Reduce the positive symptoms of schizophrenia Also have numerous side effects NMDA receptor Slide 23 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Concluding Remarks Impact of neuroscience on psychiatry Mental illness Chemical synaptic transmission is affected by drugs Genes and environment play an important role Environmental stresses may contribute to schizophrenia Appropriate sensory stimulation in early childhood Slide 24 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins End of Presentation Slide 25 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins