* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture Note
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive memory wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
Collective memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
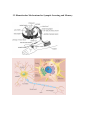
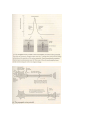
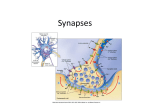
Lecture 4 (Wed, 9/10) Chapter 3: Biological Basis of Learning and Memory 3.1 Memory Networks in the Brain 3.2 Biomolecular Mechanisms for Synaptic Learning and Memory 3.3 Principles of Molecular Information Processing for Learning and Memory 3.1 Memory Networks in the Brain Physical Scales in Computational Neurobiology organ system (cm) Information Processing increasing structural realism cellular (mm to μm) subcellular (μm to nm) molecular (angstroms) Neural Networks Groups of Neurons Single Neurons Groups of Synapses Single Synapses Groups of Neurotransmitters (molecules) Molecular Dynamics Memory Networks at Three Levels - Cortical network (between the cell assemblies) - Synaptic network (between the cells) - Molecular network (within a cell) 3.2 Biomolecular Mechanisms for Synaptic Learning and Memory Note: Figures captured from [Kandel-06]. - Learning and memory can be explained at the cellular and molecular levels. - The location of learning and memory is synapses. - Learning is involved with physical change of synapses by protein synthesis. - Molecular information processing such as chemical synaptic transmission involves with memory and learning. Chemical nature of information processing in the brain - - Electrical signals at the cellular level are based on the chemistry at the molecular level. - Thus, modeling the information processing in the brain at the molecular level may shed light on that at the cellular level. - Related question: Explaining the properties of matter based on particles in physics - Understanding the structure of composite material based on atoms and molecules in chemistry. Chemical nature of synaptic transmission - The transmission of electrical signals are based on the underlying chemical signal transduction at the molecular level. - Chemistry is important in understanding the principles of cognitive learning and memory. Questions: - Is brain an electrical computer or a chemical computer? - Related question: Is light a wave or a particle? Electrical Chemical Electrical Biochemical mechanisms of short-term memory - Signal transmission in a synapse is based on the lock-key mechanism between the ligands and the receptors. - Short-term memory is stored by strengthening the chemical transmission mechanisms through secreting neurotransmitters at the synapses. - - Short-term memory does not involve nucleus but the long-term memory does. - Short-term memory involves functional changes at a single synapse, but long-term memory changes the anatomical or structural changes of the synapses. Long-term memory and gene expression (Relationship between synapse and gene) Q: How the proteins synthesized can be transported to the synapses to learn? Note: Signal broadcasting in a radio station A: The synthesized proteins are transported to various synapses, but the synapses that are stimulated by serotonins receive the proteins and grow the axon terminals. 9/22 (Mon) 3.3 Principles of Molecular Information Processing for Learning and Memory Visualization of Synaptic Cleft