* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Brain Facts - The Practice of Parenting
Craniometry wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
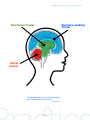
6 BRIDGE STREET · SAN ANSELMO · CA · 94960 · PH 415 578 0522 · TAYLOR @ THEPRACTICEOFPARENTING.COM WWW.THEPRACTICEOFPARENTING.COM Basic facts about the human brain • The human brain is about the size of a coconut, the shape of a walnut, and the consistency of a ripe peach. • Humans are one of the only animals in nature born without a fully developed brain. 75% of our brain develops after birth. 90% of our brain develops before the age of 10. However, crucial processes that sculpt our brains occur in the teenage years and throughout our 20’s. • Human brain growth occurs from bottom up - with the most primitive functions first and the most advanced reasoning and decision making abilities last. • When we talk about brain growth, we are mainly talking about growing connections between neurons. Connections between neurons are made through electrical and chemical signals. • Strong connections between neurons are made when we do things again and again, and when we have big feelings while we experience something. • Our brains are shaped by our biology (genes), our environment, and our experiences. • The way we are with each other, our repetitive interactions, and our thoughts shape our brains. In every moment, we are all brain sculptors. • The human brain can grow, change, and heal throughout all of our life, but is most capable of and susceptible to change in the early years. • A baby is born with 100 billion neurons in it’s brain. That is as many as there are stars in the sky, and like the stars, the neurons are not yet connected. • By the age of three, we have 1,000 trillion (a quadrillion) connections between neurons. • By the age of three, the connections that are the weakest start to get pruned. This allows the brain to operate more efficiently. The strongest connections, those associated with emotion and repetition, remain. • Myelin is a slippery substance that covers our neural pathways to help them connect more quickly. A well used path becomes myelinated for brain efficiency. • In our teen years our brains go through a big remodel - there is a massive pruning process, new grey matter is grown in the thinking part of our brains, myelin sheaths cover the neural pathways in our lower and middle brains. However, the “upstairs brain” is not yet complete and is not yet maturely myelinated until our late 20’s. Page 1 of 3 TAYLOR ROSS | THE PRACTICE OF PARENTING Functions of the brain Built from the bottom up Alarm Center Brain Stem, cerebellum, reptilian brain, hindbrain, etc... • Fight, Flight, Freeze, Collapse • What functions at birth? • Body regulation (heartbeat, digestion, reflexes, etc...) • Primarily lit up at 0-1 years Emotional Center Mid-brain, Limbic system, hippocampus, amygdala, etc... • Generate emotion • Feelings, feelings, feelings • Relationships • Imagination • Memory • Sense of self • Build bridges to upstairs brain • Primarily lit up 1-6 • “Name it to tame it” recognizing feelings when they arise - ex “There is a feeling of frustration”, as apposed to I am my frustration. Decision-making Center Forebrain, upstairs brain, cortex, etc... • Last to develop in primates • Gives us the ability to: • Pause before acting, impulse control • Reason, decision making, weighting consequences • Self soothing fibers • Empathy and compassion • Morality • Connection to a larger whole • Coach for whole brain, regulates sub cortical brain • Spurts in development - big in adolescence • Supported development through mindfulness Adapted from original material by ECHO Parenting & Education Page 2 of 3 TAYLOR ROSS | THE PRACTICE OF PARENTING Decision-making Center Emotional Center Alarm Center “Our greatest glory is not in never falling, but in rising every time we fall.” Confucious Page 3 of 3