* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dissection of the Sheep Brain
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
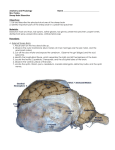
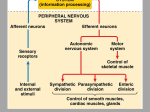
Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain. 2. Identify and locate the main structures in the human brain by viewing an actual human brain from a cadaver using Anatomy & Physiology Revealed, Version 2.0 CD. 3. Describe the functions of the main structures of the sheep brain and human brain discussed in lab. 4. Identify the cranial nerves and describe their functions. INTRODUCTION The human brain is the largest and most complex organ of the nervous system. It weights about 3 pounds in an average adult and is mainly composed of nervous tissue. It is made up of about 100 billion neurons and approximately 900 billion neuroglia cells. The brain is responsible for body sensations and perception, initiates and coordinates muscle contractions and body functions, and carries on higher mental abilities, such as thinking, memory, etc. The brain is divided in four parts: (1) cerebrum; (2) brainstem, which consist of midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata; (3) diencephalon, which consists of the thalamus and hypothalamus; and (4) cerebellum. Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the underside of the brain: 2 pairs arise from the cerebrum and 10 pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brainstem. These cranial nerves are designated by numbers and names. The number indicates the order in which the nerve arises from the brain, form anterior to posterior. The name comes from the primary functions or general distribution of the cranial nerve. In this laboratory, you will dissect the main parts of the sheep brain. Most of these parts are similar in structure to the human brain while some are not. However, the sheep brain is an excellent organ used to understand the mammalian brain structures and functions. Therefore, the parts of the sheep brain that you will dissect will be compared with those of the human brain in structure and function. You will also identify parts of the human brain by viewing an actual brain from a cadaver by using your Anatomy & Physiology Revealed, Version 2.0 CD. 1 Procedure PART A NOTE: use TABLE 1.1 to describe functions and appearance or characteristics for each part of the sheep brain that you dissect. Meninges, Cerebrum, Cerebellum & Spinal Cord 1. Obtain a preserved sheep brain. 2. Examine the surface of the sheep brain for the presence of meninges. Most likely you will only see the pia mater as the outermost layers (dura mater and arachnoid mater) were lost in the removal process of the sheep brain from the cranial cavity. Dura Mater Use the pointed prove to pick a piece of pia mater at several parts of the brain and also at the spinal cord. Pia Mater Sheep Brain 3. Position the sheep brain with its anterior surface on the dissecting tray. Locate the following structures: Cerebrum Cerebellum Spinal Cord Posterior View 2 PART B Cerebrum 1. With the sheep’s brain anterior surface on the dissecting tray, identify and locate the longitudinal fissure, the 2 cerebral hemispheres (right and left cerebral hemispheres), and the transverse fissure. Longitudinal Fissure Left Cerebral Hemisphere Use the blunt prove to pierce through the pia mater at the surface of the longitudinal fissure. Notice that the 2 fissures you are observing are deep grooves. Right Cerebral Hemisphere Transverse Fissure Spinal Cord Posterior View 2. Identify gyri and sulci at the cerebrum of the sheep brain. Gyrus = singular Gyri = plural Sulcus = singular Sulci = plural Gyri Sulci How are gyri of the human brain different from the ones on the sheep’s brain? ________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ Use the blunt prove to pierce through the pia mater on the surface of sulci. Notice that sulci are shallow grooves. Posterior View 3 3. The cerebrum is divided in 5 lobes: Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital, and Insula. In the lab you will only locate and identify the following 4 lobes of the cerebrum: Frontal Lobe-lateral view Parietal Lobe-lateral view Temporal Lobe-lateral view Occipital Lobe-lateral view NOTE: Do other views of the sheep brain to identify lobes: superior, inferior views 4. Grab the cerebrum and the cerebellum and GENTLY bend downward the two of them. This will expose the corpora quadrigemina (four rounded structures that make up the midbrain of the brainstem). Notice that on the superior portion of the corpora quadrigemina you will see the pineal gland. Pineal Gland Cerebrum Midbrain Cerebellum 4 5. With the anterior portion of the sheep’s brain on the dissecting tray, CAREFULLY remove a slice from the parietal lobe using the scapel. Notice the white matter (cerebral medulla) and the gray matter (cerebral cortex) of the cerebrum. cerebral cortex (gray matter) ? What structure or structures of the neuron are found in the gray mater of the cerebrum? What structure or structures of the neuron are found in the white matter of the cerebrum? cerebral medulla (white matter) Which matter makes up the MAIN bulk of the cerebrum? Posterior View 6. Using the figure below: A. LABEL: cerebral cortex, cerebral medulla, gyri, cerebrum and cerebellum. B. DRAW: 1) the structures or parts of the neuron found in the cerebral cortex. 2) the structure or part of the neuron found in the cerebral medulla. NOTE: review the three (3) main structures of the neuron in Figure 10.1, pg. 355, of your A&P textbook. ? Circle One: a) The cerebral medulla is made of white/gray matter. b) The cerebral cortex is made of white/gray matter. c) Does the cerebellum have.. white matter? Yes No gray matter? Yes No Posterior Anterior Midsagittal Section of the Human Brain 5 7. Position the sheep’s brain on the dissecting tray with its anterior surface upward. Identify the following structures: Olfactory nerve (bulb) Longitudinal fissure Olfactory tract Optic chiasma Optic nerve Optic tract Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Anterior View PART C Brainstem: composed of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata 1. Position the sheep’s brain on the dissecting tray with its anterior surface upward. Identify the three structures that make up the brainstem. Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Anterior View 6 Brainstem 2. Position the sheep brain with its anterior surface on the dissecting tray. Using the scalpel CAREFULLY cut the sheep brain along the longitudinal fissure and continue then through the midline of the cerebellum and spinal cord to produce a midsagittal section of the brain and spinal cord. Longitudinal Fissure 3. Locate the following parts in the midsagittal section of the sheep brain. Cerebrum Pineal Gland Corpora quadrigemina of midbrain Cerebellum Spinal cord Optic nerve Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Brainstem Midsagittal Section 7 PART D Diencephalon: composed of Thalamus and Hypothalamus 1. Locate the 2 structures that make up the diencephalon in the longitudinal section of the sheep brain. Thalamus Diencephalon Hypothalamus Midsagittal Section PART E Cerebrum: Revisited! 1. Identify the following structures found in the cerebrum. Corpus callosum Use your blunt prove and insert it inside the corpus callosum to find the lateral ventricle. Lateral ventricle (cavity) Midsagittal Section 8 PART F Cerebellum 1. Identify the gray matter (cerebellar cortex) and white matter (cerebellar medulla) of the cerebellum. Cerebellar cortex (gray matter) Cerebellum Midsagittal Section Cerebellar medulla (white matter) Note: the white matter pattern in the cerebellum is called arbor vitae. ? What structure or structures of the neuron are found in the gray matter of the cerebellum? What structure or structures of the neuron are found in the white matter of the cerebellum? 2. LABEL: cerebellum, cerebellar cortex, and cerebellar medulla in this midsagittal section the human Whichofmatter makesbrain. up the main bulk of the cerebellum? Posterior Anterior Midsagittal Section of the Human Brain 9 Exercises 1. LABEL: the structures in this midsgittal section of the right half of the human brain. E A. _____________________________ F B . _____________________________ C. _____________________________ A D J D. _____________________________ E. _____________________________ B C G F. (cavity)_______________________ G. _____________________________ H K L H. _____________________________ I. ______________________________ I Anterior M Posterior J. ______________________________ K. _____________________________ L. (fissure)_______________________ M. _____________________________ 2. LABEL: the lobes of the human cerebrum. 10 3. IDENTIFY: write the name of the brain structures or parts described below. ______________a) A mass of white fibers connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres. ______________b) A fold of cortical gray matter on the surface of the cerebrum ______________c) The middle of three divisons of the brainstem. ______________d) The gray matter on the surface of the cerebrum. ______________e) The gray matter on the surface of the cerebellum. ______________f) The white matter on the cerebrum. ______________g) The white matter on the cerebellum. ______________h) Fissure dividing the cerebrum and the cerebellum. ______________ i) Area where the optic nerves cross. 4. LABEL: the structures of the brain by placing the correct name next to the spaces provided. Skull Meninges 11