* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 090309-presentation
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
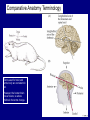
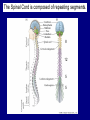
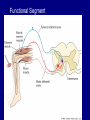
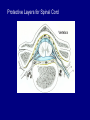
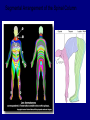
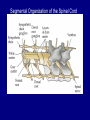
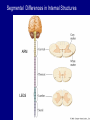
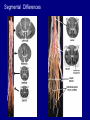
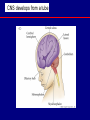
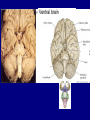
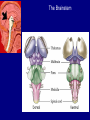
QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/Pages/ lavaillab/index.html) Comparative Anatomy Terminology Terms used for brain and entire body are consistent in rat. However, the human brain has a flexure, so above midbrain the terms change. The horizontal plane of the cerebral cortex is a longituinal plane in the spinal cord. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. BIG PICTURE The Spinal Cord is composed of repeating segments. 8 12 5 5 Plan of the Spinal Cord Each segment has the same elements. Somatosensory afferents (fibers that come into the CNS) Motoneuron axons or efferents (fibers that exit the CNS). Interneurons (cells whose axons do not leave the CNS. Repeating Plan of the Spinal Cord Somatosensory afferents have their cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglion outside of the CNS. The afferents enter the spinal cord and synapse on the same side of the cord. The motor neurons that innervate muscles (smooth or striated) are located on the same side of the cord as are the muscles. The interneurons have axons that synapse with other interneurons or with motor neuron cells. Functional Segment Protective Layers for Spinal Cord Vertebra Segmental Arrangement of the Spinal Column Segmental Organization of the Spinal Cord Segmental Differences in Internal Structures ARM LEGS Segmental Differences B CNS develops from a tube Origins of Brain Divisions Brain stem Ventral brain The Brainstem