* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
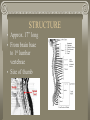
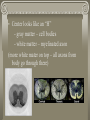
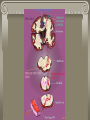
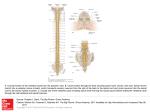
WARM UP 3/17 1. What is a Schwann cell? 2. What are interneurons? 3. What are the 2 divisions of the autonomic? 4. What are the 3 meninges in order? 5. What is the sympathetic system? 6. Name 3 things that the sympathetic does? NOTES CH 10: 3/17 SPINAL CORD FUNCTION 1. Brings messages to and from the brain 2. Reflex center STRUCTURE • Approx. 17” long • From brain base to 1st lumbar vertebrae • Size of thumb • Center looks like an “H” - gray matter – cell bodies - white matter – myelinated axon (more white mater on top – all axons from body go through there) TRACTS = bundles of nerves 1. ASCENDING TRACTS – carry impulses up the sp cord (afferent neurons) 2. DESCENDING TRACTS – carry impulses down the sp cord (efferent neurons) A pair of SPINAL NERVES exit from each segment of the sp cord 31 pairs total: 8 prs – cervical nerves 12 prs – thoracic 5 prs – lumbar 5 prs – sacral 1 coccygeal EXTRA CREDIT OPP. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves…… If you can memorize all 31 in 2 minutes, then you get an ec slip….BUT If you don’t get them all, then you have to lose 5 participation points from your grade. WHO WANTS TO PLAY????????????? SPINAL CORD NERVE NAMES C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8 T1, T2, T3….. T12 1L, 2L …5L 1S, 2S …. 5 S coccygeal PARALYSIS – if sp cord cut or crushed, loss of senses and motor of area below it PARAPLEGIC – legs paralyzed QUADRAPLEGIC – arms and legs paralyzed LABELING 1. Dura mater 2. Subdural space 3. Arachnoid 4. Pia mater 5. Skin 6. Periosteum 7. Bone Dura mater 9. Arachnoid 10. Pia mater 8. 11. Spinal cord 12. Dorsal root 13. Ventral root ** Central canal 14. Dura mater 15. Arachnoid 16. Pia mater 17. Spinal nerves 18. vertebrae (bone) On labeling sheet HOW A MESSAGE TRAVELS THROUGH THE BODY 1. Stimulus detected by receptors 2. Impulse travels through afferent neurons to spinal cord (* see steps through a neuron) 3. Ascending tract up spinal cord to brain 4. Brain interprets message 5. MESSAGE CAN STOP HERE OR CAUSE A REACTION 6. Brain sends response 7. Descending tract down spinal cord from the brain 8. Impulse travels through efferent neurons to muscle or gland 9. Body response