* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous Tissue: Support Cells
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
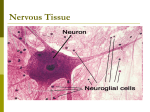
Nervous Tissue: Neuroglia = Support Cells Support cells in the Central Nervous System (CNS) are grouped together as neuroglia Neuroglia literally means “nerve glue” The function of neuroglia is to support, insulate, and protect the delicate neurons of the brain Types of Neuroglia in CNS Astrocytes – Star-shaped cells – Half of all brain tissue – Brace neurons; they keep the neurons in contact with their blood supply (capillaries) – Control the chemical environment of the brain by mopping up leaked ions Types of Neuroglia in CNS Microglia – Spiderlike phagocytes (white blood cells) – Dispose of debris like dead brains cells and bacteria Types of Neuroglia in CNS Ependymal cells – Lines the cavities of the brain and spinal cord – Circulate cerebrospinal fluid by beating their cilia – Cerebrospinal fluid fills the space the brain does not take up and forms a protective cushion around the brain and spinal cord Types of Neuroglia in CNS Oligodendrocytes – Wrap around nerve cells in the brain and spinal chord – Produce myelin sheaths for spinal cord and brain (CNS) – Myelin is a fatty, insulation covering the nerve cells; allows for the electrical signal to transmit faster (like wire coating) Types of Neurolgia in PNS Schwann cells – Form myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system (nerves of the body; not nerves of the CNS) So what’s a Neuron? Neurons are nerve cells – Cells specialized to transmit messages – Major parts of neurons Cell body — nucleus and metabolic center of the cell (main part of nerve cell) Processes — fibers that extend from the cell body (where messages sent or received) – can be microscopic or up to 3-4 feet in length Anatomy of a Neuron Cell body – Nucleus Processes cell body outside the – Dendrites — send impulses toward the cell body – Axons — send impulses away from the cell body Anatomy of a Neuron Axons end in axon terminals Axonal terminals contain small sacs with neurotransmitters (chemicals) Synapse and Synaptic Cleft Axonal terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap (they never really touch) – Synaptic cleft — gap (space) between adjacent neurons – Synapse — junction between nerves What happens at a synapse? For communication between neurons to occur, an electrical impulse must travel down an axon to the synaptic terminal. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft . They bind with receptor sites on the other neurons’ dendrite.s This influences the electrical response in the neuron. If enough neurotrasmitter is released, it changes the cell's excitability This allows for the signal to move on to the next neuron Multiple Sclerosis MS affects the ability of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord to communicate with each other. In MS, the body's own immune system attacks and damages the myelin