* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
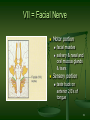
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
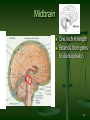
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
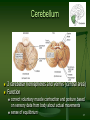
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
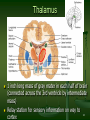
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
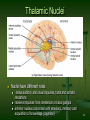
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
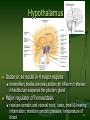
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
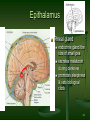
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
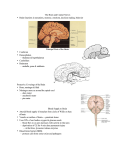
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
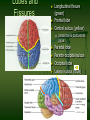
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
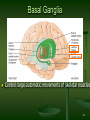
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
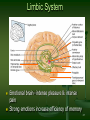
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
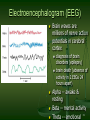
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
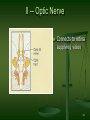
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
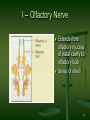
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
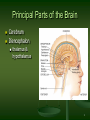
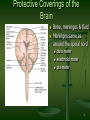
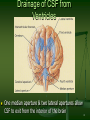
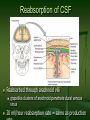
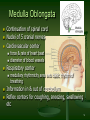
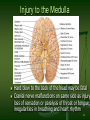
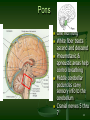
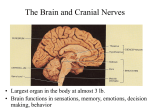
Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum Diencephalon thalamus & hypothalamus 1 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body at almost 3 lb. Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 2 Protective Coverings of the Brain Bone, meninges & fluid Meninges same as around the spinal cord dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater 3 Blood Supply to Brain Arterial blood supply is branches from circle of Willis on base of brain (page 699) Vessels on surface of brain----penetrate tissue Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanent injury at that time, lysosome release enzymes Blood-brain barrier (BBB) protects cells from some toxins and pathogens proteins & antibiotics can not pass but alcohol & anesthetics do 4 Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) 80-150 ml (3-5oz) Clear liquid containing glucose, proteins, & ions Functions mechanical protection chemical protection floats brain & softens impact with bony walls optimal ionic concentrations for action potentials circulation nutrients and waste products to and from 5 Drainage of CSF from Ventricles One median aperture & two lateral apertures allow CSF to exit from the interior of the brain 6 Reabsorption of CSF Reabsorbed through arachnoid villi grapelike clusters of arachnoid penetrate dural venous sinus 20 ml/hour reabsorption rate = same as production 7 Hydrocephalus Blockage of drainage of CSF (tumor, inflammation, developmental malformation, meningitis, hemorrhage or injury Continued production cause an increase in pressure --- hydrocephalus In newborn or fetus, the fontanels allow this internal pressure to cause expansion of the skull and damage to the brain tissue Neurosurgeon implants a drain shunting 8 Medulla Oblongata Continuation of spinal cord Nuclei of 5 cranial nerves Cardiovascular center Respiratory center force & rate of heart beat diameter of blood vessels medullary rhythmicity area sets basic rhythm of breathing Information in & out of cerebellum Reflex centers for coughing, sneezing, swallowing etc 9 XII = Hypoglossal Nerve Controls muscles of tongue during speech and swallowing Injury deviates tongue to injured side when protruded Mixed, primarily motor 10 X = Vagus Nerve Receives sensations from viscera Controls cardiac muscle and smooth muscle of the viscera Controls secretion of digestive fluids 11 IX = Glossopharyngeal Nerve Stylopharyngeus m. (lifts throat during swallowing) Secretions of parotid gland Somatic sensations & taste on posterior 1/3 of tongue 12 Injury to the Medulla Hard blow to the back of the head may be fatal Cranial nerve malfunctions on same side as injury loss of sensation or paralysis of throat or tongue; irregularities in breathing and heart rhythm 13 Pons One inch long White fiber tracts ascend and descend Pneumotaxic & apneustic areas help control breathing Middle cerebellar peduncles carry sensory info to the cerebellum Cranial nerves 5 thru 7 14 VII = Facial Nerve Motor portion facial muscles salivary & nasal and oral mucous glands & tears Sensory portion taste buds on anterior 2/3’s of tongue 15 Midbrain One inch in length Extends from pons to diencephalon 16 Cerebellum 2 cerebellar hemispheres and vermis (central area) Function correct voluntary muscle contraction and posture based on sensory data from body about actual movements sense of equilibrium 17 Thalamus 1 inch long mass of gray mater in each half of brain (connected across the 3rd ventricle by intermediate mass) Relay station for sensory information on way to 18 cortex Thalamic Nuclei Nuclei have different roles relays auditory and visual impulses, taste and somatic sensations receives impulses from cerebellum or basal ganglia anterior nucleus concerned with emotions, memory and acquisition of knowledge (cognition) 19 Hypothalamus Dozen or so nuclei in 4 major regions mammillary bodies are relay station for olfactory reflexes; infundibulum suspends the pituitary gland Major regulator of homeostasis receives somatic and visceral input, taste, smell & hearing information; monitors osmotic pressure, temperature of 20 blood Functions of Hypothalamus Controls and integrates activities of the ANS which regulates smooth, cardiac muscle and glands Synthesizes regulatory hormones that control the anterior pituitary Contains cell bodies of axons that end in posterior pituitary where they secrete hormones Regulates rage, aggression, pain, pleasure & arousal Feeding, thirst & satiety centers Controls body temperature 21 Epithalamus Pineal gland endocrine gland the size of small pea secretes melatonin during darkness promotes sleepiness & sets biological clock 22 Subthalamus & CVO Circumventricular organs sites of entry of HIV virus into brain (dementia) 23 Cerebrum (Cerebral Hemispheres) Cerebral cortex is gray matter overlying white matter 2-4 mm thick containing billions of cells grew so quickly formed folds (gyri) and grooves (sulci or fissures) Longitudinal fissure separates left & right cerebral hemispheres Corpus callosum is band of white matter connecting left and right cerebral hemispheres Each hemisphere is subdivided into 4 lobes 24 Lobes and Fissures Longitudinal fissure (green) Frontal lobe Central sulcus (yellow) precentral & postcentral gyrus Parietal lobe Parieto-occipital sulcus Occipital lobe Lateral sulcus (blue) Temporal lobe Insula 25 Basal Ganglia Control large automatic movements of skeletal muscles 26 Limbic System Emotional brain--intense pleasure & intense pain Strong emotions increase efficiency of memory 27 Brain Injuries Causes of damage Concussion---temporary loss of consciousness displacement or distortion of tissue at impact increased intracranial pressure infections free radical damage after ischemia headache, drowsiness, confusion, lack of concentration Contusion--bruising of brain (less than 5 min unconsciousness but blood in CSF) Laceration--tearing of brain (fracture or bullet) increased intracranial pressure from hematoma28 Aphasia Language areas are located in the left cerebral hemisphere of most people Inability to use or comprehend words = aphasia nonfluent aphasia = inability to properly form words know what want to say but can not speak damage to Broca’s speech area fluent aphasia = faulty understanding of spoken or written words faulty understanding of spoken or written words word deafness = an inability to understand spoken words word blindness = an inability to understand written words damage to common integrative area or auditory 29 Hemispheric Lateralization Functional specialization of each hemisphere more pronounced in men Females have larger connections between 2 sides Damage to left side produces aphasia Damage to same area on right side produces speech with little emotional inflection 30 Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brain waves are millions of nerve action potentials in cerebral cortex diagnosis of brain disorders (epilepsy) brain death (absence of activity in 2 EEGs 24 hours apart) Alpha -- awake & resting Beta -- mental activity 31 Theta -- emotional II -- Optic Nerve Connects to retina supplying vision 32 I -- Olfactory Nerve Extends from olfactory mucosa of nasal cavity to olfactory bulb Sense of smell 33 Dorsal View of Neural Groove 34 Aging & the Nervous System Years 1 to 2 rapid increase in size due to increase in size of neurons, growth of neuroglia, myelination & development of dendritic branches Early adulthood until death brain weight declines until only 93% by age 80 number of synaptic contacts declines processing of information diminishes conduction velocity decreases 35 Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) Third leading cause of death after heart attacks and cancer 2 types of strokes Risk factors ischemic due to decreased blood flow hemorrhagic due to rupture of blood vessel high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease, diabetes, smoking, obesity, alcohol Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) used within 3 hours of onset will decrease permanent disability 36 Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) Episode of temporary cerebral dysfunction Cause Symptoms impaired blood flow to the brain dizziness, slurred speech, numbness, paralysis on one side, double vision reach maximum intensity almost immediately persists for 5-10 minutes & leaves no deficits Treatment is aspirin or anticoagulants; artery bypass grafting or carotid endarterectomy 37 Alzheimer Disease (AD) Dementia = loss of reasoning, ability to read, write, talk, eat & walk Afflicts 11% of population over 65 Loss of neurons that release acetylcholine Plaques of abnormal proteins outside neurons Tangled protein filaments within neurons Risk factors -- head injury, heredity Beneficial effects of estrogen, vitamin E, ibuprofen & ginko biloba 38