* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mrs. Walston Science
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
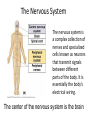
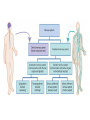
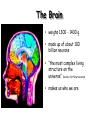
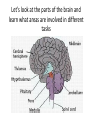
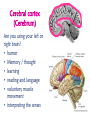
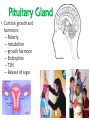
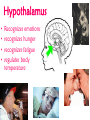
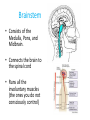
The Nervous System The nervous system is a complex collection of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It is essentially the body’s electrical wiring. The center of the nervous system is the brain The Brain • weighs 1300 - 1400 g • made up of about 100 billion neurons • “the most complex living structure on the universe” Society for Neuroscience • makes us who we are Let’s look at the parts of the brain and learn what areas are involved in different tasks Cerebral cortex (Cerebrum) Are you using your left or right brain? • humor • Memory / thought • learning • reading and language • voluntary muscle movement • interpreting the senses MEMORY BANKS – How well do you remember? • Momentary memory bank • Short-term memory bank • Long-term memory bank MOMENTARY MEMORY ACTIVITY • Jot down 20 random single digits (from 0 - 9) • Find a partner. • Partner A will tell partner B a single digit at a time. • Partner B recalls all the numbers, starting from the beginning, adding the one new digit last. • Example: Partner A: “One” Partner B: “One” Partner A: “Eight” Partner B: “One, eight” • Continue until Partner B messes up. • Record the number of digits he/she WAS able to remember without messing up. • Switch roles. • Collect class data. NUMBER OF DIGITS REMEMBERED Average TRANSFERRING INFORMATION FROM MOMENTARY TO SHORT-TERM MEMORY What techniques do you use to help you remember…….let’s try one more memory game. Study the following for one minute: You have 30 sec. to write down as many objects you can remember! What were some of your “tricks”? All those “tricks” you described are common methods for committing information to memory (learning) Process Time the period which elapses between start & finish - recognition - memory retrieval - output Let’s try an example….. Stroop Effect Corpus callosum • Connects the right side of the brain to the left side of the brain • Let’s the two sides of the brain talk to each other Cerebellum • controls balance • works with the cerebrum to produce smooth, controlled, muscle movements try to “outsmart” your foot 1. While sitting at your desk, lift your right foot off the floor and make clockwise circles with it. 2. Now, while doing this, draw the number '6' in the air with your right hand….. Your foot will change direction. You can’t do it. It's pre-programmed in your brain! Pituitary Gland • Controls growth and hormones: – Puberty – metabolism – growth hormone – Endorphins – TSH – Release of sugar Hypothalamus • • • • Recognizes emotions recognizes hunger recognizes fatigue regulates body temperature Pineal Gland • makes and secretes melatonin, which regulates bodily rhythms, including: – biological clock (sleep/wake cycle) – seasonal changes Brainstem • Consists of the Medulla, Pons, and Midbrain. • Connects the brain to the spinal cord • Runs all the involuntary muscles (the ones you do not consciously control) Pons • maintains consciousness ( being aware of ones surroundings) and sleep • controls breathing Medulla Oblongata • controls breathing & heartbeat • relays messages to spinal cord • controls reflexes: – sneezing – coughing – swallowing – sucking (in babies) – vomiting Midbrain • The midbrain controls many important functions such as the visual and auditory systems as well as eye movement. • Also plays an important role in body movement. Spinal Cord The most important body structure between the body and the brain. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system, it it the pathway to the peripheral nervous system. What protects the central nervous system? Cerebrospinal fluid • Cerebrospinal fluid is fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. • This fluid acts as a cushion, protecting the brain and spine from injury. It is like a shock absorber for your central nervous system