* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7. The Nervous System Identify the major structures and areas of the
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
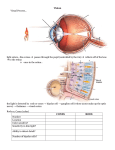
7.TheNervousSystem Identifythemajorstructuresandareasofthebrainanddescribetheirfunctions Thebrainiscomprisedofthreemainparts: 1. Forebrain o Cerebralhemispheres § Largestpartofbrainandmaintainsmuscletone,coordinatesmovementandstores memoriesofskilledmovemente.g.walkinganddriving § Fourlobes–frontal,parietal,occipital,temporal § Dividedintotwohalvesbyafurrow § Corpuscallosumisthebundleofaxonsconnectingthetwohemispheres § Greysurfacemadeofnervecells § Whitenervefibresunderneathcarrysignalsbetweennervecellsandrestofthebody o Thalamus § Axonsfromeverysensorysystemsynapseherebeforetheinformationreachesthe cerebralcortex o Hypothalamus § Involvesinhomeostasis,emotion,thirst,hungeretc. § Controlsthepituitarygland o Pinealandpituitarygland 2. Midbrain o Fibretractsconnectingthe forebraintomidand hindbrainandcolliculi 3. Hindbrain o Cerebellum(‘littlebrain’) § Twohemispheres o Brainstem § Underneaththelimbic system § Containsthemidbrain, ponsandmedulla o Pons § Involvedinmovement andposture o Medulla § Responsiblefor maintainingvitalbodyfunctionsi.e.breathingandheartrate Centralnervoussystem(CNS)–spinalcord&brain Peripheralnervoussystem(PNS)–everythingelse Structures • Meninges:protectivemembranessurroundingthebrain andspinalcordandspaceswithinthemcontainafluid calledcerebrospinalfluid(CSF) o CSFproducedbychoroidplexuscellsinthe ventricles • CSF:cushionsandprotectstheCNS,actsasamediumfor theexchangeofnutrientsandwasteproductsbetween thebloodandthebrain • Foramenmagnum:divisionbetweenthebrainandspinalcord • Intervertebralforamen:divisionbetweenthePNSandCNS Ventriclesofthebrain Brainregion Thecavitywithineachofthecerebralhemispheres Surroundedbythethalamusandhypothalamus Betweenthemedullaandcerebellum Ventricle Lateral Third Fourth Describethestructureofthespinalcord Structure Ventralroot Dorsalroot Dorsalrootganglion Spinalnerve Whitematter Motoraxons Sensoryfibres Inthegreymatteroftheanterior hornsinthespinalcord Description Containsnervefibresconductingimpulsesfromthespinalcord Containsnervefibresconductingimpulsestothespinalcord Containscellbodiesofsensoryneurons Peripheralnervecontainingbothsensoryandmotorfibres Duetothepresenceofmyelin Containedwithintheventralroot Containedwithinthedorsalroot Locationofcellbodiesofthemotorneurons 8.TheSenses Describethestructureandfunctionofthevertebrateeyeandtheresponseoftheeyetostimuli Structure Lens Function • Refractsandfocuseslightrays(magnification) • Infrontofthepupil Iris • Controlsdiameterofthepupilandtheamountoflightenteringtheeye Cornea • • • • • • • Nobloodsupply,reliesoninterstitialfluid Corneatransplantsareeasytoperform Lookstransparent Convertlighttoneuralsignalstosendtothebrainforvisualrecognition Madeupofphotoreceptors(rods),bipolarcellsandganglioncells Layerofbloodvesselswhichsupplyoxygenandnutrientstotheouterretina Betweenretinaandsclera • • • • • • • • • Toughexternalcoatthatprotectstheeyeball(whiteoftheeye) Connectivetissue Madeofganglionnervecells Transfersvisualinformationfromretinatobrainviaelectricalimpulses Providenutrientstothelensandcornea Giveshapetotheeyeball Maintainintraocularpressure Refractlight Holdlensandretinainplace Rodsandcones • Photo-receptors Pupil • Wherelightenterstheeye Blindspot • • • • • Smallareaoftheretinawithnovisualreceptors(norodsorcones) Containsnervefibresthatconductimpulsestothebrainviatheopticnerve Attacheslenstociliarymuscles Allowslenstobulgeorflattendependingonthedesireddistance Distantvisionàlensflattenàtensiononsuspensoryligamentsàciliarybodyrelaxes • • • Containssmoothmuscle Controlsthicknessofthelens Ringofmusclesurroundinglens Retina Choroid Sclera Opticnerve Aqueousand vitreoushumour Suspensory ligaments Ciliarybody Theeyehascircumductionmovement Photoreceptors:rodsandcones 1)Rods • Responsibleforvisionatlow lightlevels(scotopicvision) • Donotmediatecolourvision • Verysensitivebutlowresolution • 100millionrods • Containsproteinrhodopsin whichismadeofopsinand retinal(moleculederivedfrom Vit.A) 2)Cones • 3types:blue,green,red • Allowsmediationofcolour • Highresolutionbutinsensitive tolight • Lossofconefunctionleadstomacular degeneration • Foveacentraliscontainsonlyconesand providesthesharpestvision • 6millioncones • Proteincalledphotopsins Lightà electricalsignals • Photonsabsorbedbyrodsandcones • Phototransduction–opsinturnsthe photonsintoelectrochemicalsignals whicharesenttotheopticnervethen brain • VitaminA(coupledwithopsin)aborbsthe lightàchangesstructureàseparates fromopsinàelectricalsignalgeneratedto closeupvoltagedependentchannelsà decreasesdepolarisation • Lateralgeniculatebody(inthethalamus) receivessensoryinputfromtheopticnervetotheoccipitalbone Thevisualpathway • • • Opticnerveàopticchiasmaàoptictractà superiorcolliculus(involvedinvisualreflexes) àthalamusàoccipitallobeàvisualcortex StructurespartofthePNS–retina,opticnerve StructurespartoftheCNS–optictract, colliculi,thalamus,visualcortex Hearingdefects Conductiondeafness–occurswhensoundwavesfail tobeconductedfromthetympanicmembranetothe cochlea.Canbecausedbyfluidbuild-up(replacingair), traumaordiseasecausingfibrousscartissuein ossicleswalls Nervedeafness–occurswhenthecochlea,orthe cranialnervesfromit,aredamagedtoimpulsesfailto reachtheauditorycortexofthebrain.Suchpersonisunabletohearsound.