* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chromatin Structure and Gene Regulation
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
DNA methylation wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetyltransferase wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
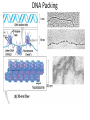
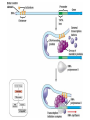
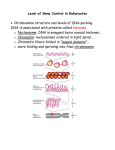
Eukaryotic Genome Structure and Gene Regulation 19.1 & 19.2 Lesson 4.6 Chromatin • Chromatin – DNA/protein complex in eukaryotic cells • All the DNA in a cell, if spread out, would be thousands of times longer than the diameter of the cell – which is why chromatin folding is necessary DNA Packing Cell Differentiation • Cells which produce proteins which are very specialized to its function – e.g. muscle cells • Almost all cells of an organism have an identical genome, but only certain genes are expressed in each type of cell – Differential gene expression – cause of expression of different genes by cells with the same genome Where Gene Regulation Occurs Types of Regulation • Regulation on Chromatin Structure – Histone modifications – DNA Methylation • Regulation of Transcription Initiation • Post-Transcriptional Regulation – RNA Processing – mRNA Degradation – Initiation of Translation – Protein Processing and Degredation Regulation of Chromatin Structure: Histone Modifications • Histone Acetylation – attaching an acetyl group to the end of a histone, neutralizing these ends so they cannot bind to other nucleosomes – This gives transcription proteins easier access to genes – If histones are deacetylated, transcription of those genes cannot occur Regulation of Chromatin Structure: DNA Methylation • Methylation (attachment of a methyl group to DNA) causes most genes to be inactive • Removal of the methyl group on these genes will cause expression • Methylation or demethylation during embryonic development is responsible for if maternal or paternal alleles are expressed – genomic imprinting Transcription of the Eukaryotic Genome • Transcription Factors must be in place for polymerases to act, but most transcription factors cannot recognize promoters in the same way that enzymes do mRNA Degradation • In prokaryotic cells, mRNA degrades quickly, within minutes, of being in the cytoplasm • In eukaryotes, it could be up to weeks, allowing them to be translated multiple times if necessary – When it is degraded, enzymes shorten the poly-A tale and 5’ Cap, allowing the mRNA to be degraded – There are nucleotide sequences in the poly-A tail that code for how long it will be until it is degraded (scientists removed those sequences and immediately it degraded)