* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download «題目»
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
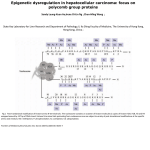
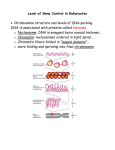
Genome-wide functional analysis of a histone modification 高承福 中央研究院細胞與個體生物所 Abstract The molecular basis of epigenetics involves modifications to DNA and histone proteins that associate with the regulation of gene expression but that do not result from mutation or changes to the DNA sequence. The four core histone proteins are subject to post-translational modifications, such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation and ubiquitylation. To understand how histone modifications regulate gene transcription, we analyzed transcriptional profiling in wild type and four yeast mutant strains, in which histone H3 K4, K79, K4/79 methylations and H2B K123 ubiquitylation (ub) were eliminated respectively. Statistical analysis of microarray data revealed significantly altered genes in these experiments. Hierarchical clustering was applied and it suggested that H2Bub regulated gene transcription independently of H3K4 methylation. Our analysis also linked H2Bub to specific regulation of Ribosomal protein genes (RPG) expression. RPG transcription is rapidly and coordinately regulated in response to a variety of environmental alterations. Despite the importance of coordinated regulation of RPGs, its mechanism remains incomplete. To gain insight of H2Bub in transcriptional regulation, genome-wide ChIP-chip assay was used to identify the distribution of H2Bub in the yeast genome. ChIP-chip data were extracted using computational algorithms, and further graphical tools showed that the levels of H2Bub were enriched throughout the transcribed regions. H2Bub also preferentially correlated with highly transcribed genes, including RPG. Taken together, using two genome wide approaches, we have identified a central role for H2Bub in regulating the specialization of RPG transcription.