* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Epigenetic regulators as novel treatments
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
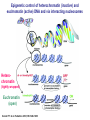
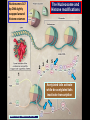
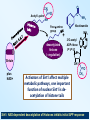
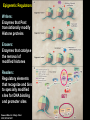
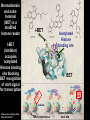
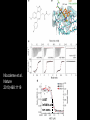
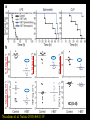
Epigenetic regulators as novel treatments for sepsis (Grant in collaboration with GSK) S. Opal Toronto CCCF Oct. 27, 2015 Some definitions: Epigenetics-the study of heritable changes in gene expression without changing the DNA sequence; this occurs at 3 levels of organization: 1) methylation of cytosine nucleotides within coding sequences and at promoter sites that alter transcription rates 2) changes in chromatin protein structure and function-usually post - translational modifications of histone protein tails: the acetylated histone targets by Sirt-1 or i-BET compounds 3) silencing sequences of non-coding RNA-microRNAs Epigenetic control of heterochromatin (inactive) and euchromatin (active) DNA and via interacting nucleosomes Heterochromatin (tightly wrapped) Euchromatin (open) Cornell T T et al. Pediatrics 2010;125:1248-1258 1o 2o 3o Activating transcription factor 3 CCAAT/enhancer-binding factor d Minutes: proinflammatory Hours: anti-inflammatory + host defense genes 1o response genes 2o/3oresponse genes: de novo synthesis Days: mixed response + immunometabolic genes Positive-transcription elongation factor b BRM-related gene 1 Transcriptional start site Medzhitov&Horng 2009;9:692 The Nucleosome and Histone modifications Nucleosomes 147 bp DNA tightly wrapped around histone octamers 2 3 4 5 1 Acetylated tails activate while de-acetylated tails inactivate transcription Dawson N Engl J Med 2012;367:647 O CH3 Acetyl Lysine O C NH2 NH Free e amino group + deacetylated histone (- regulation) + N Nicotinamide NH2 2’O-acetyl ADP ribose P’-P’-O Sirtuin N N N N O OH O O plus NAD+ Activators of Sirt1 affect multiple metabolic pathways, one important function of nuclear Sirt1 is deacetylation of histone tails CH3 Sirt1: NAD-dependent deacetylation of Histones inhibits initial APP response Epigenetic Regulators Writers: Enzymes that Post translationally modify Histone proteins Erasers: Enzymes that catalyse the removal of modified histones Readers: Regulatory elements that recognize and bind to specially modified sites for DNA binding and promoter sites Dawson MA et al. N Engl J Med 2012;367:647-657 BET Bromodomain and extraterminaI (BET) is a modified histone reader i-BET I-BET (inhibitor) occupies acetylated Histone binding site blocking BET recognition of start signal for transcription Acetylated Histone binding site BET Activate Dawson et al. N Engl J Med 2012;367:647-657 RNA polymerase Transcriptional start site Nicodeme et al. Nature 2010;468:1119 i-BET inhibits at nm conc. i-BET rapidly alters the transcription of ≈300 inflammatory genes induced by LPS Similar data for Sirt1 activators given early (anti-inflammatory), or Sirt1 inhibitors given late to reconstitute the inflammatory response (McCall et al. Exp Rev Clin Immunol 2014;10 (9):1-10) Nicodeme et al. Nature 2010;468:1119 KC (IL-8) Nicodeme et al. Nature 2010;468:1119 IBET12102013 Delayed Rx (6-24h after CLP) with antibiotics alone vs antibiotics and i-BET Kaplan-M eier Survival Curve * 1. 00 I bet10Mox206hr n=10 * S urvi val 0. 75 Mox206hr n=10 I bet10Mox2012hr n=10 0. 50 Mox2012hr n=10 I bet10Mox2024hr n=5 0. 25 Mox2024hr n=5 0. 00 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 168 Hours *No antibiotic control (n=5) no survivors at 96hr; Moxi-moxifloxacin Can iBET and other epigenetic therapies targeting histones succeed where other immune modulators have failed in sepsis? -they have proven to be tolerable in oncology patients -Sirt1 and i-BET alter a wide spectrum of acute inflammatory genes -potentially fewer off target effects than corticosteroids -can be given after insult and can still work as salvage Rx DNA NFkB nuclear localization sequence 5’ 3’ 5’ 3’ Host response and antimicrobial defense programs