* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download APBio-StudyGuide-Ch18
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
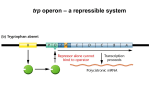
AP Biology Chapter 18 Study Guide Name 1. What are the two ways that metabolic control can occur within bacteria? 2. What is the key advantage of grouping genes of related function in to one transcription unit? 3. What does the operator control, and where is it located? 4. What is the name for the operator, promoter, and the genes they control? 5. What can happen if the trp operan is turned “on”? 6. What turns the “switch” off and how? 7. What gene controls the making of the trp repressor protein? 8. How is the trp repressor protein and allosteric protein? 9. Explain what positive and negative gene feedback are and how they work. 10. Why is the trp operon considered repressible? 11. What does the inducer do? 12. Why are repressible enzymes generally associated with anabolic pathways and how is this an advantage to the organism? 13. DNA can exist as heterochromatin or euchromatin. Which is transcribed and why? 14. What is cell differentiation? 15. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? 16. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? 17. What effect do the following have on gene expression? a. Histone acetylation b. Histone de-acetylation c. DNA methylation 18. What is genomic imprinting, and how does methylation relate to it? 19. What is epigenetics and why does it matter? 20. How do the following control elements assist in regulation? a. Transcription factors b. Enhancers c. Activators d. Repressors 21. Use the diagram below to explain the interactions of enhancers and transcription activators. 22. Explain how RNA processing is a mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation. 23. What role do microRNA’s play in post-transcriptional regulation? Use the diagram below to help you explain. 24. What is RNA interference? 25. How does translation provide another opportunity for control? 26. What is a proteasome? 27. What is the difference between oncogenes,proto-oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes? 28. What are ras and p53 genes? 29. Why is said that people inherit predispositions to cancer not cancer itself? 30. What is the difference between transposons and retrotransposons. Use the diagram below to help you answer the question. 31. What are multi-gene families? 32. What are pseudogenes? 33. How can errors during meiosis lead to duplication of genes? 34. What are three ways transposable elements are thought to have contributes to the evolution of the genome?