* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson1 Powerpoint
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Response priming wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Visual extinction wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
C1 and P1 (neuroscience) wikipedia , lookup
Efficient coding hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
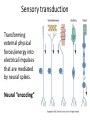
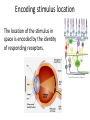
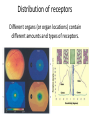
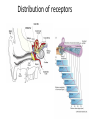
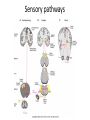
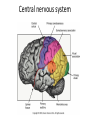
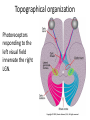
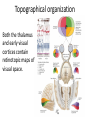
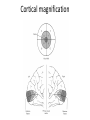
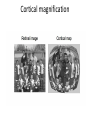
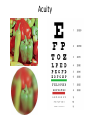
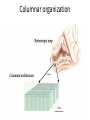
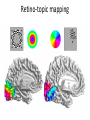
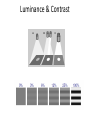
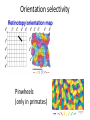
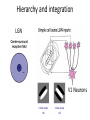
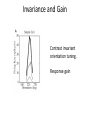
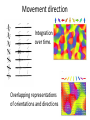
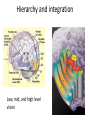
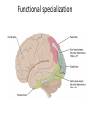
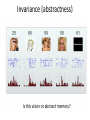
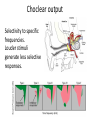
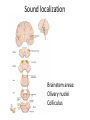
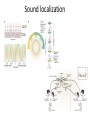
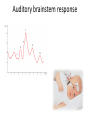
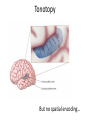
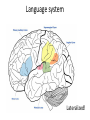
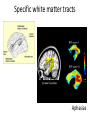
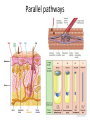
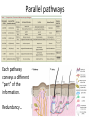
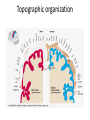
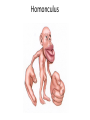
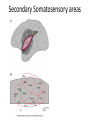
Sensory systems basics Sensing the external world Sensory transduction Transforming external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” Encoding stimulus amplitude Responses of a photoreceptor to light at different intensities. Information is encoded by both amplitude and length of the response. Encoding stimulus location The location of the stimulus in space is encoded by the identity of responding receptors. Encoding stimulus location Encoding stimulus location Distribution of receptors Different organs (or organ locations) contain different amounts and types of receptors. Distribution of receptors Distribution of receptors Sensory pathways Sensory pathways Central nervous system Vision Topographical organization Photoreceptors responding to the left visual field innervate the right LGN. Topographical organization Both the thalamus and early visual cortices contain retinotopic maps of visual space. Occular dominance Information from the left and right eyes remains segregated in the LGN. Occular dominance Also in primary visual cortex. Cortical magnification Cortical magnification Acuity Columnar organization Selectivity to stimulus attributes Spatial receptive fields Contrast Luminance Spatial frequency Orientations Colors Movement direction and/or speed Textures Shapes Receptive field Many visual neurons have excitatory and inhibitory parts to their receptive field. Examples of retinal and LGN cells. Retino-topic mapping Luminance & Contrast Orientation selectivity Orientation selectivity in primary visual cortex. Orientation selectivity Pinwheels (only in primates) Hierarchy and integration LGN V1 Neurons Invariance and Gain Contrast invariant orientation tuning. Response gain Contrast Spatial frequency Integration over space. Spatial frequency Movement direction Integration over time. Overlapping representations of orientations and directions Hierarchy and integration Low, mid, and high level vision Functional specialization Face selectivity Invariance (abstractness) Is this vision or abstract memory? Audition Choclear output Selectivity to specific frequencies. Louder stimuli generate less selective responses. Sound localization Interaural time differences (ITD) Sound localization Brainstem areas: Olivary nuclei Colliculus Sound localization Auditory brainstem response Tonotopy But no spatial encoding… Language system Lateralized! Language structure Phonetics: ‘ba’, ‘da’, ‘pa’ Words, Grammar, Intonation How is all this encoded? Language hierarchy? Invariance across hearing and reading? Specific white matter tracts Aphasias Somatosensation Parallel pathways Parallel pathways Each pathway conveys a different “part” of the information. Redundancy… Topographic organization Homonculus Secondary Somatosensory areas How does all this develop? Genetics Experience Flexibility/Plasticity