* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Brain
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
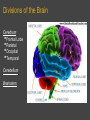
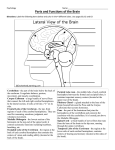
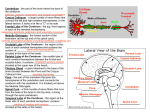
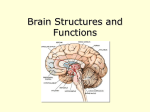
The Human Brain General Information about the Brain • Two types of cells • • • • • o gray - unmylinated o white - mylinated Dura matter - surrounds the brain and connects to the skull. It also surrounds the spinal cord Two Hemispheres - Right and left Corpus callosum - allows the two hemispheres to communicate Cerebrospinal fluid - cycles around through the ventricles (open spaces) in the brain and through the central canal of the spinal cord Blood - brain barrier - specialized cells prevent materials from entering the brain - a form of protection Divisions of the Brain Cerebrum Frontal Lobe Parietal Occipital Temporal • • • • Cerebellum Brainstem Cerebrum • General info: • • • • o largest division of the brain o folds increase surface area for neurons (ridges = gyri, sulcus = grooves, fissure = deep groove) o Fissure separates the left and right hemispheres and the cerebrum from the cerebellum Frontal Lobe - concentration, planning, voluntary motor areas Parietal Lobe - sensation of temperature, touch, pain Occipital Lobe - visual center of the brain Temporal Lobe -auditory center of the brain Curious Facts about the Cerebrum Right brain - Left brain The areas responsible for speaking are on the left. Also on the left side are the areas responsible for analytical thinking and math skills The right hemisphere mainly deals with nonverbal, motor tasks. Example: understanding the body's position in space, interpreting music, emotional and intuitive thoughts • • This is the case for most people, but not everyone! • The right side of the body is controlled by the left side of the brain and vice versa What Happens if the Sides of the Brain Cannot Communicate? •This can result from a split-brain operation. This procedure is done to treat severe forms of epilepsy where the seizures are unable to be controlled in any other way. In the operation the corpus callosum is cut and signals are no longer able to be sent from one side to the other. • Check out this video How do they figure all this out? Through disease, injuries, and medical experimentation Watch These.. Cerebellum • also called the "tree of life", because of its appearance when cut • processes information about the position of the body • damage causes inability to balance, walk properly, and can even result in shaking (tremors) Brainstem Midbrain reflex center o Makes the eyes move as the head turns o Makes the head move to better locate sound o Helps to maintain posture • Pons relay center to the higher portions of the brain and the other portions of the brainstem • Medulla Oblongata relays signals to the spinal cord and to the cerebellum regulates involuntary motor functions o heart rate o dilation and constriction of blood vessels o breathing • •